网页制作网站建设公司it人必看的网站
paper:FoveaBox: Beyond Anchor-based Object Detector
code:https://github.com/taokong/FoveaBox
背景
基于anchor的检测模型需要仔细设计anchor,常用方法之一是根据特定数据集的统计结果确定anchor的number、scale、ratio等,但这种针对特定数据集的设计并不总能适用于其它数据集,泛化性较差。另外训练阶段anchor-based的模型通常根据和GT的IoU来定义正负样本,这又引入了额外的计算和超参。
本文的创新点
受到人眼中心凹(fovea)区域的启发:视野中心区域的视觉灵敏度最高,本文提出了一种新的anchor-free的目标检测方法FoveaBox,FoveaBox联合预测对象中心区域可能存在的位置以及每个有效位置处的边界框。在FoveaBox中,每个目标对象通过中心区域的类别得分进行预测,同时预测bounding box,训练阶段不需要使用anchor或是IoU匹配来生成训练目标,训练目标是根据GT box直接生成的。
方法介绍
给定一个GT box \((x_{1},y_{1},x_{2},y_{2})\),首先将其映射到特征金字塔的目标层 \(P_{l}\)
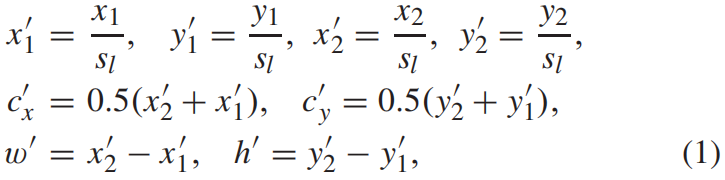
其中 \(s_{l}\) 是下采样步长。定义输出特征图上对应GT box中心区域为正样本区域 \(R^{pos}\)
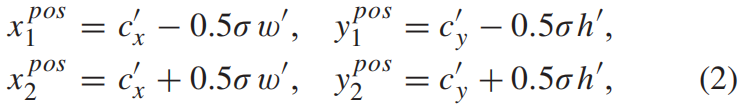
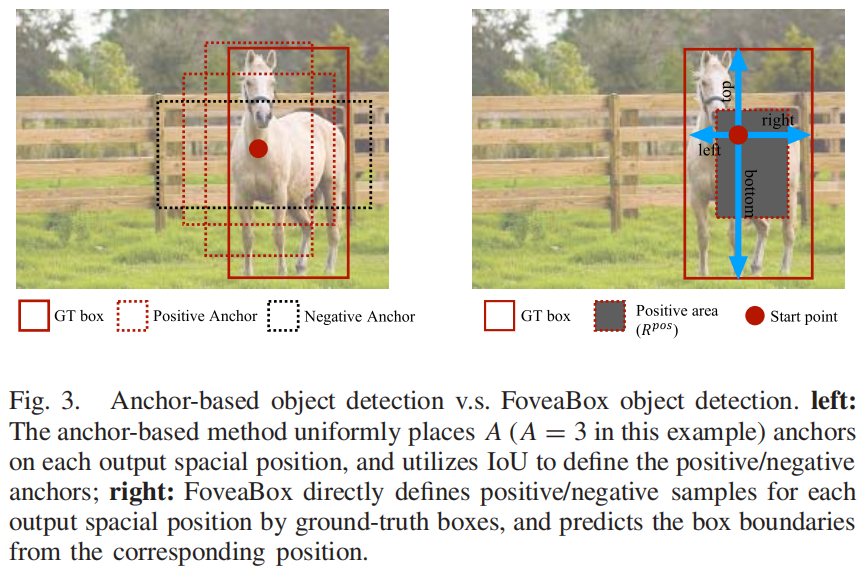
其中 \(\sigma\) 是收缩系数,文中 \(\sigma = 0.4\)。训练阶段,正样本区域内的每个像素位置都标为对应的目标类别标签,整个特征图上,除了正样本区域其它都是负样本区域。如下图右灰色区域所示

在标签分配中,除了按上述对正负样本区域进行了限制,还对FPN每层负责预测的目标大小即scale进行了限制。对于FPN的输出层 \(P_{3}-P_{7}\),每一层的basic scale \(r_{l}\) 为32至512。\(l\) 层的有效scale区间按下式计算得到

其中 \(\eta \) 是超参,文中 \(\eta =2\)。注意和之前一个目标只会由特征金字塔中的某一层负责预测的方法不同,FoveaBox中一个目标可能会由FPN的多层负责预测。将目标分配给多个相邻的FPN层有两个优点:(1)相邻的特征金字塔层通常具有相似语义表示能力,因此FoveaBox可以同时优化这些相邻层的特征。(2)FPN每一层的训练样本数量增大,使得训练过程更加稳定。
对于一个GT box \(G=(x_{1},y_{1},x_{2},y_{2})\),\(R_{pos}\) 区域中某一点 \((x,y)\) 的回归target即到四条边界的归一化的偏移按下式得到
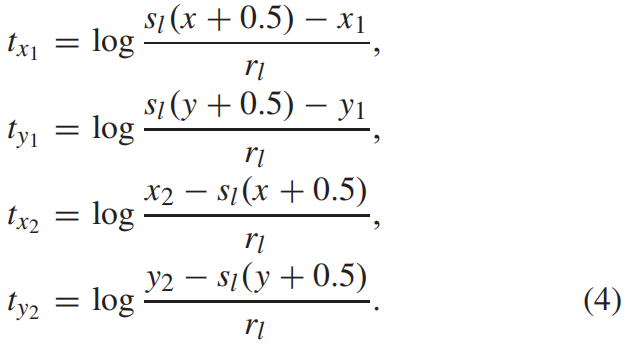
FoveaBox的结构如下图所示,整体结构和anchor数量为1的RetinaNet是一样的,只不过在样本分配和定义上又区别。

代码解析
这里以mmdet中的实现为例,代码文件在https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection/blob/master/mmdet/models/dense_heads/fovea_head.py,foveabox相对于retinanet的创新点就在于anchor-free以及对应的标签分配部分,这里的核心代码在函数_get_target_single()中,这个函数的作用就是就算FPN输出层中的单层分类和回归的target,完整代码如下
def _get_target_single(self,gt_bboxes_raw,# (2,4), tensor([[52.5, 46.8, 235.7, 274.4], [101.7, 29.6, 221.7, 175.8]], device='cuda:0')gt_labels_raw, # (2), tensor([12, 14], device='cuda:0')featmap_size_list=None,point_list=None):
gt_areas = torch.sqrt((gt_bboxes_raw[:, 2] - gt_bboxes_raw[:, 0]) *(gt_bboxes_raw[:, 3] - gt_bboxes_raw[:, 1])) # torch.Size([2])
label_list = []
bbox_target_list = []
# for each pyramid, find the cls and box target
# self.base_edge_list=[16, 32, 64, 128, 256]
# self.scale_ranges=((1, 64), (32, 128), (64, 256), (128, 512), (256, 2048)), 注意收尾本来分别为16和1024,这里改为了1和2048
# self.strides=[8, 16, 32, 64, 128]
for base_len, (lower_bound, upper_bound), stride, featmap_size, \points in zip(self.base_edge_list, self.scale_ranges,self.strides, featmap_size_list, point_list):# FG cat_id: [0, num_classes -1], BG cat_id: num_classespoints = points.view(*featmap_size, 2) # (1444,2) -> (38,38,2)x, y = points[..., 0], points[..., 1] # (38,38),(38,38)labels = gt_labels_raw.new_zeros(featmap_size) + self.num_classes # (38,38), 值全为self.num_classesbbox_targets = gt_bboxes_raw.new(featmap_size[0], featmap_size[1],4) + 1 # (38,38,4),值全为1# scale assignmenthit_indices = ((gt_areas >= lower_bound) &(gt_areas <= upper_bound)).nonzero().flatten() # torch.Size([1]), tensor([1], device='cuda:0')if len(hit_indices) == 0:label_list.append(labels)bbox_target_list.append(torch.log(bbox_targets))continue_, hit_index_order = torch.sort(-gt_areas[hit_indices])hit_indices = hit_indices[hit_index_order] # 按面积从大到小排列gt_bboxes = gt_bboxes_raw[hit_indices, :] / stridegt_labels = gt_labels_raw[hit_indices]half_w = 0.5 * (gt_bboxes[:, 2] - gt_bboxes[:, 0])half_h = 0.5 * (gt_bboxes[:, 3] - gt_bboxes[:, 1])# valid fovea area: left, right, top, downpos_left = torch.ceil(gt_bboxes[:, 0] + (1 - self.sigma) * half_w - 0.5).long(). \clamp(0, featmap_size[1] - 1)pos_right = torch.floor(gt_bboxes[:, 0] + (1 + self.sigma) * half_w - 0.5).long(). \clamp(0, featmap_size[1] - 1)pos_top = torch.ceil(gt_bboxes[:, 1] + (1 - self.sigma) * half_h - 0.5).long(). \clamp(0, featmap_size[0] - 1)pos_down = torch.floor(gt_bboxes[:, 1] + (1 + self.sigma) * half_h - 0.5).long(). \clamp(0, featmap_size[0] - 1)for px1, py1, px2, py2, label, (gt_x1, gt_y1, gt_x2, gt_y2) in \zip(pos_left, pos_top, pos_right, pos_down, gt_labels,gt_bboxes_raw[hit_indices, :]):labels[py1:py2 + 1, px1:px2 + 1] = labelbbox_targets[py1:py2 + 1, px1:px2 + 1, 0] = \(x[py1:py2 + 1, px1:px2 + 1] - gt_x1) / base_lenbbox_targets[py1:py2 + 1, px1:px2 + 1, 1] = \(y[py1:py2 + 1, px1:px2 + 1] - gt_y1) / base_lenbbox_targets[py1:py2 + 1, px1:px2 + 1, 2] = \(gt_x2 - x[py1:py2 + 1, px1:px2 + 1]) / base_lenbbox_targets[py1:py2 + 1, px1:px2 + 1, 3] = \(gt_y2 - y[py1:py2 + 1, px1:px2 + 1]) / base_lenbbox_targets = bbox_targets.clamp(min=1. / 16, max=16.) # 文中有这个限制吗?label_list.append(labels)bbox_target_list.append(torch.log(bbox_targets))
return label_list, bbox_target_list下面是根据FPN某一层对应的尺度限制取出该层负责预测的GT box的index,即上面的式(3),代码如下
hit_indices = ((gt_areas >= lower_bound) &(gt_areas <= upper_bound)).nonzero().flatten() 下面是按式(2)计算 \(R^{pos}\) 区域的坐标,self.sigma是收缩系数 \(\sigma\),式(3)中是以gt box的中心坐标为基准计算的,而下面的实现是以gt box的左上角坐标为基准计算的。
# valid fovea area: left, right, top, down
pos_left = torch.ceil(gt_bboxes[:, 0] + (1 - self.sigma) * half_w - 0.5).long(). \clamp(0, featmap_size[1] - 1)
pos_right = torch.floor(gt_bboxes[:, 0] + (1 + self.sigma) * half_w - 0.5).long(). \clamp(0, featmap_size[1] - 1)
pos_top = torch.ceil(gt_bboxes[:, 1] + (1 - self.sigma) * half_h - 0.5).long(). \clamp(0, featmap_size[0] - 1)
pos_down = torch.floor(gt_bboxes[:, 1] + (1 + self.sigma) * half_h - 0.5).long(). \clamp(0, featmap_size[0] - 1)下面是按式(4)计算回归target,其中base_len即这一层对应的basic scale \(r_{l}\)。
for px1, py1, px2, py2, label, (gt_x1, gt_y1, gt_x2, gt_y2) in \zip(pos_left, pos_top, pos_right, pos_down, gt_labels,gt_bboxes_raw[hit_indices, :]):labels[py1:py2 + 1, px1:px2 + 1] = labelbbox_targets[py1:py2 + 1, px1:px2 + 1, 0] = \(x[py1:py2 + 1, px1:px2 + 1] - gt_x1) / base_lenbbox_targets[py1:py2 + 1, px1:px2 + 1, 1] = \(y[py1:py2 + 1, px1:px2 + 1] - gt_y1) / base_lenbbox_targets[py1:py2 + 1, px1:px2 + 1, 2] = \(gt_x2 - x[py1:py2 + 1, px1:px2 + 1]) / base_lenbbox_targets[py1:py2 + 1, px1:px2 + 1, 3] = \(gt_y2 - y[py1:py2 + 1, px1:px2 + 1]) / base_len这里有一些疑问,一是下面这行对回归target进行大小的限制论文中好像没有提到
bbox_targets = bbox_targets.clamp(min=1. / 16, max=16.)二是mmdet中对FPN每一层的basic scale \(r_{l}\) 以及负责预测目标的valid scale range和论文中有些差异,如下

其中base_edge_list就是每一层的 \(r_{l}\),如果按照文中计算方式,实际的valid scale range应该如下

如果以设定的scale_ranges为准,则实际的 \(r_{l}\) 应该是[32, 64, 128, 256, 512],并且第一个值由16改为了1,最后一个值由1024改为2048。
实验结果
Comparision with SOTA
下面是FoveaBox和当时的一些SOTA方法的对比,可以看出FoveaBox取得了最优的精度,而且好于当时刚刚提出的其它anchor-free方法比如CornerNet和ExtremeNet。