网站建设全网营销客户资源南京seo网站优化
ThinkPHP6 模型层的模型属性,表映射关系,以及模型层的CRUD及如何在控制层中使用模型层
1. model 模型层的默认映射规则
模型,即mvc模式中的model层,model层用来对接数据库,操作数据库的增删改查。
在tp6中,模型会自动对应数据表,模型类的命名规则是除去表前缀的数据表名称,采用驼峰法命名,并且首字母大写的方式。(和控制层,视图层一样,也需要导入相应的类库think\Model)。
模型名与数据库的对应关系,例如下表:
| 模型名 | 约定对应数据表(假设数据库的前缀定义是 robin_) |
|---|---|
| User | robin_user |
| StudentInfo | robin_student_info |
当然也可以不像上面这样写,这时候就需要自己在对应的模型类中,通过属性protected $table = "xxx"来设定。
2. 举例:自定义model映射表名
假定你的表名叫stu_info,然后你的模型类为Student,那么为了使其相对应,就需要修改一下属性。那么写个小例子测试一下:
config/database.php 默认配置:
<?phpreturn [// 默认使用的数据库连接配置'default' => env('database.driver', 'mysql'),// 自定义时间查询规则'time_query_rule' => [],// 自动写入时间戳字段// true为自动识别类型 false关闭// 字符串则明确指定时间字段类型 支持 int timestamp datetime date'auto_timestamp' => true,// 时间字段取出后的默认时间格式'datetime_format' => 'Y-m-d H:i:s',// 时间字段配置 配置格式:create_time,update_time'datetime_field' => '',// 数据库连接配置信息'connections' => ['mysql' => [// 数据库类型'type' => env('database.type', 'mysql'),// 服务器地址'hostname' => env('database.hostname', '127.0.0.1'),// 数据库名'database' => env('database.database', 'phpdemo'),// 用户名'username' => env('database.username', 'root'),// 密码'password' => env('database.password', 'root'),// 端口'hostport' => env('database.hostport', '3306'),// 数据库连接参数'params' => [],// 数据库编码默认采用utf8'charset' => env('database.charset', 'utf8'),// 数据库表前缀 设定为 robin_'prefix' => env('database.prefix', 'robin_'),// 数据库部署方式:0 集中式(单一服务器),1 分布式(主从服务器)'deploy' => 0,// 数据库读写是否分离 主从式有效'rw_separate' => false,// 读写分离后 主服务器数量'master_num' => 1,// 指定从服务器序号'slave_no' => '',// 是否严格检查字段是否存在'fields_strict' => true,// 是否需要断线重连'break_reconnect' => false,// 监听SQL'trigger_sql' => env('app_debug', true),// 开启字段缓存'fields_cache' => false,],// 更多的数据库配置信息],
];
model层
<?php
namespace app\model;use think\Model; // 引入模型基类class Student extends Model
{// 将数据表名设定为为指定的 stu_info ,如果不配置的话,我们找到的对应的表名应为robin_studentprotected $table = "stu_info";public function queryAll(){$data = Student::select();return $data->toArray();}
}控制器层
<?php
namespace app\controller;use app\BaseController;
use app\model\Student;
use think\facade\View; // 使用模板引擎
use think\model;class test extends BaseController{public function index(){// 这里拿控制器测试一下,能否查到正确的数据$model = new Student();$data = $model->queryAll();dump($data) ;}
}
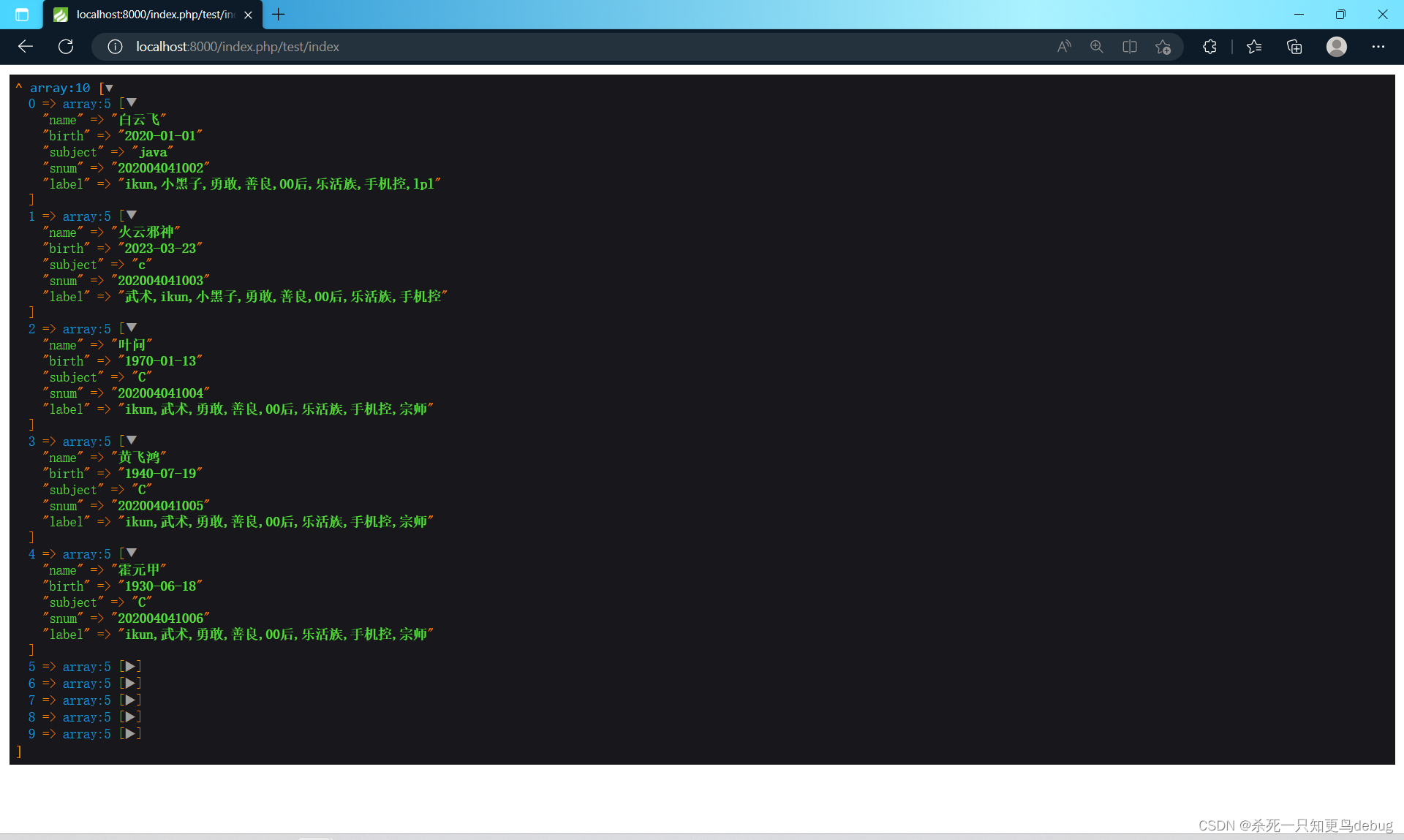
成功查到,这里只是顺带说明一下,后面会详细的说…
3. 如何在控制器中使用模型层
在控制器中使用模型层,只需要将think\model引入,然后在控制器的方法中实例化模型对象即可.
单应用目录结构如下:
在app目录下,controller ,view ,model处于同级目录。
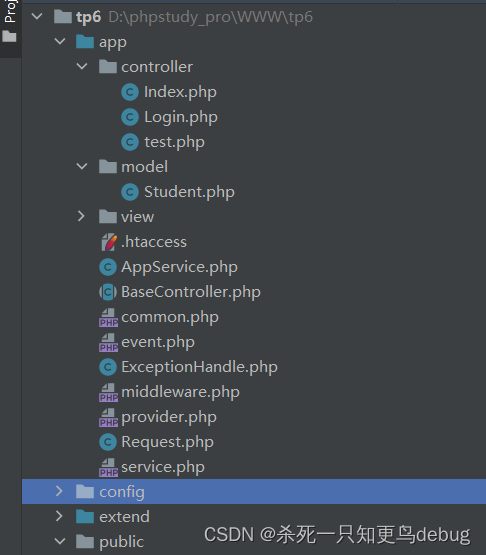
控制器:
<?php
namespace app\controller;use app\BaseController;
use app\model\Student;
use think\model; // 使用模型class test extends BaseController{public function index(){// 实例化模型层对象$model = new Student();// 调用模型对象的方法$data = $model->queryAll();dump($data) ;}
}
模型层:
<?php
namespace app\model;use think\Model; // 引入模型基类class Student extends Model
{protected $table = "stu_info";public function queryAll(){$data = Student::select();return $data->toArray();}
}
4. 模型层设置属性(自定义表名,主键…)
常用的模型设置属性包括(以下属性都不是必须设置的,是为了灵活的结合项目使用):
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| name | 模型名(相当于不带数据表前后缀的表名,默认为当前模型类名) |
| table | 数据表名(默认自动获取) |
| suffix | 数据表后缀(默认为空) |
| pk | 主键名(默认为id) |
| connection | 数据库连接(默认读取数据库配置) |
| query | 模型使用的查询类名称 |
| field | 模型允许写入的字段列表(数组) |
| schema | 模型对应数据表字段及类型 |
| type | 模型需要自动转换的字段及类型 |
| strict | 是否严格区分字段大小写(默认为true) |
| disuse | 数据表废弃字段(数组) |
上述的模型设置属性,都可以自定义配置,即修改默认的模型设置。
假定我现在有一张下面的数据表(vendors),其中主键为vend_id(与默认配置不符合)
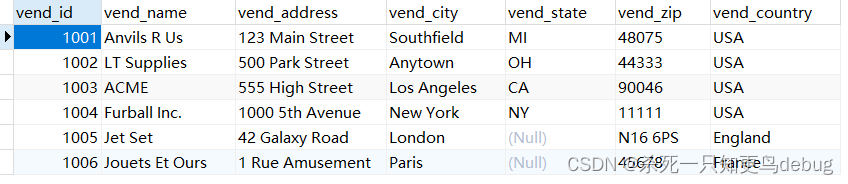
那么我的模型层可以修改成下面的样子
<?php
namespace app\model;use think\Model; // 引入模型基类class Vendors extends Model
{// 自定义表名protected $table = "vendors";// 自定义主键名protected $pk = "vend_id";public function queryAll(){// 查询主键为1002的数据信息$data = Vendors::find("1002");return $data->toArray();}
}
写个控制器测试下:
<?php
namespace app\controller;use app\BaseController;
use app\model\Vendors;
use think\model;class test extends BaseController{public function index(){$model = new Vendors();$data = $model->queryAll();// 输出dump($data) ;}
}
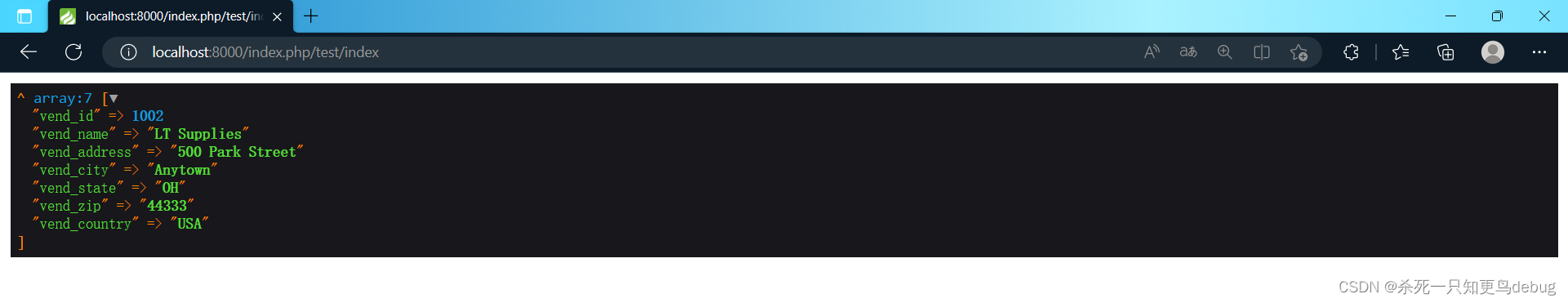
其余的模型设置也是一样,根据自己不同的需求去进行修改对应的属性即可。
5. 模型的crud 增删改查
5.1 新增数据 create saveAll
新增数据的最佳实践原则:使用create方法新增数据,使用saveAll批量新增数据。
create
create 为 类提供的静态方法,可以直接通过类名来调用。
create 方法源码如下:
/*** 写入数据* @access public* @param array $data 数据数组* @param array $allowField 允许字段* @param bool $replace 使用Replace* @param string $suffix 数据表后缀* @return static*/
public static function create(array $data, array $allowField = [], bool $replace = false, string $suffix = ''): Model
{$model = new static();if (!empty($allowField)) {$model->allowField($allowField);}if (!empty($suffix)) {$model->setSuffix($suffix);}$model->replace($replace)->save($data);return $model;
}
根据源码,我们只需要将新增的数据封装为一个数组即可完成最简单的添加,例如:
<?php
namespace app\model;use think\Model; // 引入模型基类class Student extends Model
{protected $table = "stu_info";// ...// 新增一个添加表数据的方法public function insertSt(){$st = Student::create(['name'=>'张张','birth'=>time("y-m-d"),'subject'=>'php','snum'=>'202004041020','label'=>'测试新增']);// 这里将st对象返回return $st;}
}
控制器修改调用一下:
<?php
namespace app\controller;use app\BaseController;
use app\model\Student;
use app\model\Vendors;
use think\model;class test extends BaseController{public function index(){$model = new Student();$data = $model->insertSt();// 打印数据dump($data) ;}
}
测试一下,新增成功
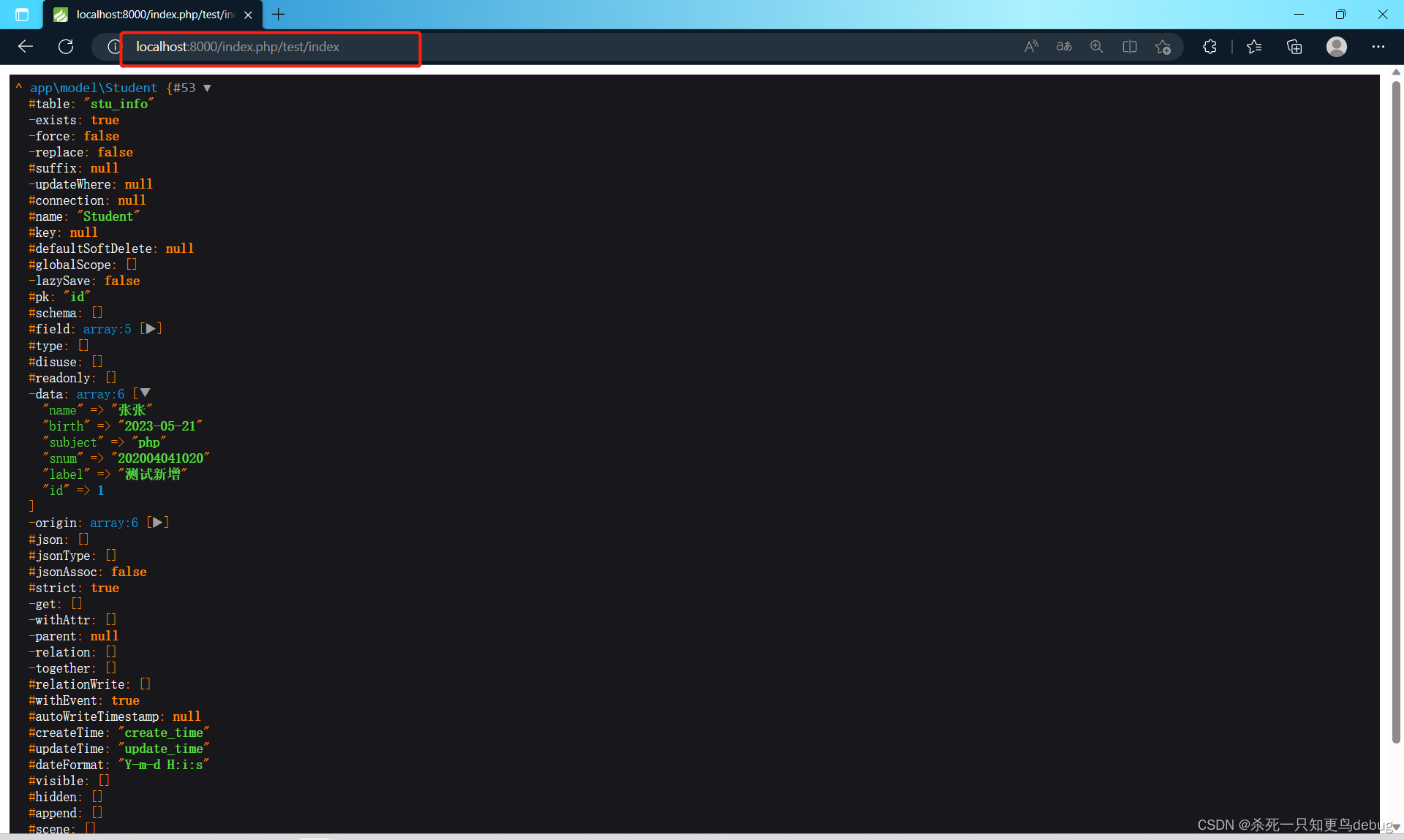
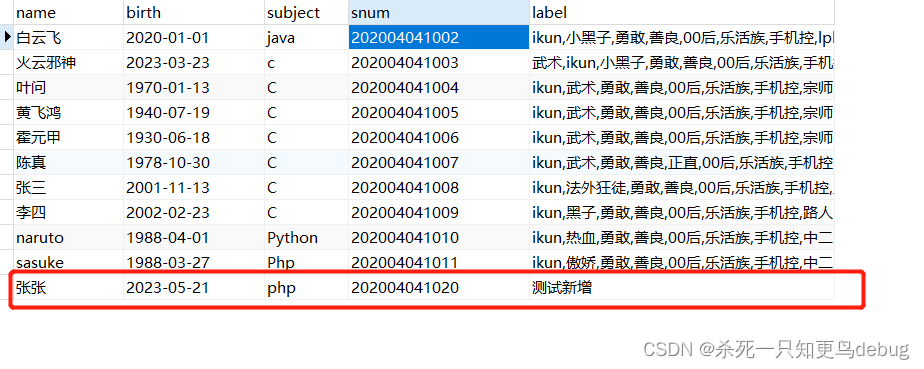
saveAll
saveAll方法新增数据默认会自动识别数据是需要新增还是更新操作,当数据中存在主键的时候会认为是更新操作。
saveAll方法新增数据返回的是包含新增模型(带自增ID)的数据集对象。
saveAll方法需要类模型对象来调用,不是静态方法。
saveAll源码:
/*** 保存多个数据到当前数据对象* @access public* @param iterable $dataSet 数据* @param boolean $replace 是否自动识别更新和写入* @return Collection* @throws \Exception*/
public function saveAll(iterable $dataSet, bool $replace = true): Collection
{$db = $this->db();$result = $db->transaction(function () use ($replace, $dataSet) {$pk = $this->getPk();$result = [];$suffix = $this->getSuffix();// 迭代器foreach ($dataSet as $key => $data) {if ($replace) {$exists = true;foreach ((array) $pk as $field) {// 主键判断,设定existsif (!isset($data[$field])) {$exists = false;}}}// 判断主键是否存在,存在则为更新操作if ($replace && !empty($exists)) {$result[$key] = static::update($data, [], [], $suffix);} else {$result[$key] = static::create($data, $this->field, $this->replace, $suffix);}}return $result;});return $this->toCollection($result);
}
分析下源码,为啥saveAll可以批量添加数据,是因为其内部有一个iterable的迭代器,然后在迭代过程中进行了一些判断是否使新增还是更新操作,以完成批量新增。
前面的例子使用了create添加单个数据,现在我们使用saveAll来批量添加数据:
模型:
<?php
namespace app\model;use think\Model; // 引入模型基类class Student extends Model
{protected $table = "stu_info";// 批量新增public function insertStMul(){$st = new Student();$list = [['name'=>'demo1','birth'=>'2023-05-21','subject'=>'php','snum'=>'202004041021','label'=>'测试批量新增1'],['name'=>'demo2','birth'=>'2023-05-21','subject'=>'php','snum'=>'202004041022','label'=>'测试批量新增2']];$coll = $st->saveAll($list);return $coll;}
}
控制器:
<?php
namespace app\controller;use app\BaseController;
use app\model\Student;
use app\model\Vendors;
use think\facade\View; // 使用模板引擎
use think\model;class test extends BaseController{public function index(){$model = new Student();$data = $model->insertStMul();dump($data) ;}
}
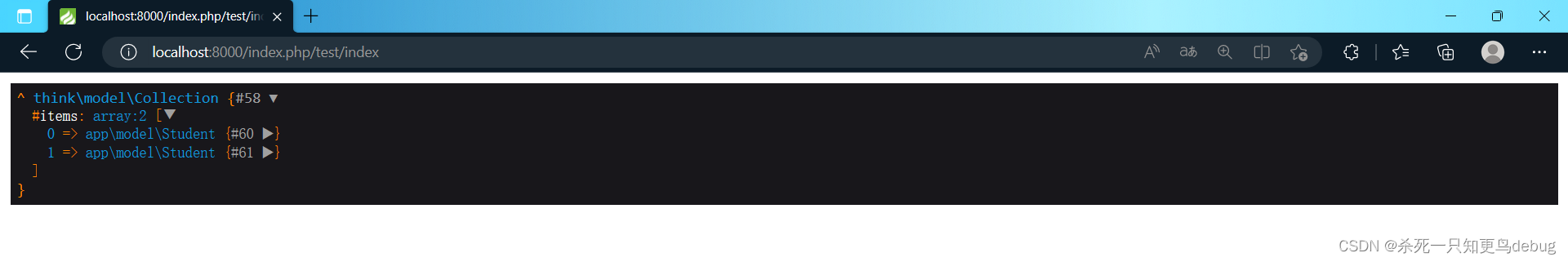
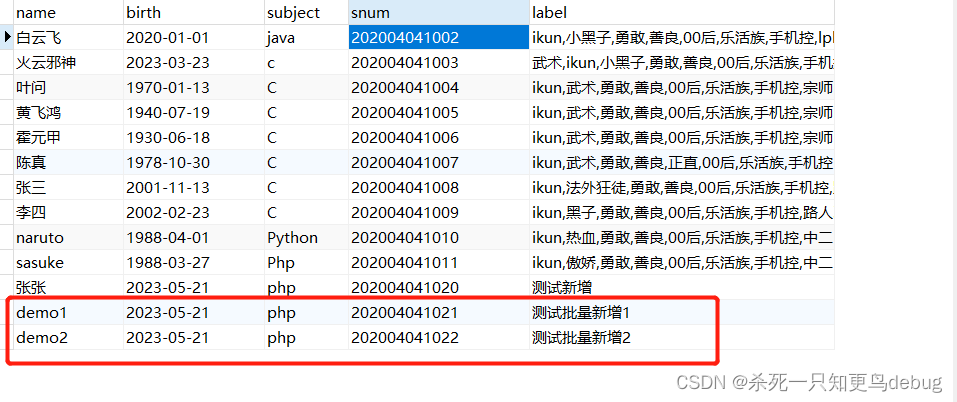
5.2 删除数据 delete destory
删除的最佳实践原则是:如果删除当前模型数据,用delete方法,如果需要直接删除数据,使用destroy静态方法。
delete
delete 方法返回值类型为布尔值,源码如下:
/*** 删除当前的记录* @access public* @return bool*/
public function delete(): bool
{if (!$this->exists || $this->isEmpty() || false === $this->trigger('BeforeDelete')) {return false;}// 读取更新条件$where = $this->getWhere();$db = $this->db();$db->transaction(function () use ($where, $db) {// 删除当前模型数据$db->where($where)->delete();// 关联删除if (!empty($this->relationWrite)) {$this->autoRelationDelete();}});$this->trigger('AfterDelete');$this->exists = false;$this->lazySave = false;return true;
}
使用delete方法()删除模型数据,可以在查询后调用delete方法。
$user = User::find(1);
$user->delete();
或者直接使用对象删除
$user = new User();
// 删除id为1 的数据
$user->where('id','=',1)->delete();
destory
destory 为静态方法,可以直接通过类来调用,然后返回值为布尔值。
当destroy方法传入空值(包括空字符串和空数组)的时候不会做任何的数据删除操作,但传入0则是有效的
源码如下:
/*** 删除记录* @access public* @param mixed $data 主键列表 支持闭包查询条件* @param bool $force 是否强制删除* @return bool*/
public static function destroy($data, bool $force = false): bool
{if (empty($data) && 0 !== $data) {return false;}$model = new static();$query = $model->db();if (is_array($data) && key($data) !== 0) {$query->where($data);$data = null;} elseif ($data instanceof \Closure) {$data($query);$data = null;}$resultSet = $query->select($data);foreach ($resultSet as $result) {$result->force($force)->delete();}return true;
}
使用destory()方法时,直接通过类调用即可(根据主键删除)
User::destroy(1);
// 支持批量删除多个数据
User::destroy([1,2,3]);
destory()闭包删除的方式:
User::destroy(function($query){$query->where('id','>',10);
});
5.3 修改更新数据 save update
更新的最佳实践原则是:如果需要使用模型事件,那么就先查询后更新(save),如果不需要使用事件或者不查询直接更新,直接使用静态的Update方法进行条件更新,如非必要,尽量不要使用批量更新。
save 先查询后更新(推荐)
在取出数据后,更改字段内容后使用save方法更新数据。这种方式是最佳的更新方式。
$user = User::find(1);
$user->name = 'thinkphp';
$user->email = 'thinkphp@qq.com';
$user->save();
save方法成功返回true,并只有当before_update事件返回false的时候返回false,有错误则会抛出异常。
tip:save方法更新数据,只会更新变化的数据,对于没有变化的数据是不会进行重新更新的。
save源码:
/*** 保存当前数据对象* @access public* @param array $data 数据* @param string $sequence 自增序列名* @return bool*/
public function save(array $data = [], string $sequence = null): bool
{// 数据对象赋值$this->setAttrs($data);if ($this->isEmpty() || false === $this->trigger('BeforeWrite')) {return false;}$result = $this->exists ? $this->updateData() : $this->insertData($sequence);if (false === $result) {return false;}// 写入回调$this->trigger('AfterWrite');// 重新记录原始数据$this->origin = $this->data;$this->get = [];$this->lazySave = false;return true;
}
update 直接更新
使用模型的静态update方法更新:
User::update(['name' => 'thinkphp'], ['id' => 1]);
模型的
update方法返回模型的对象实例
如果你的第一个参数中包含主键数据,可以无需传入第二个参数(更新条件)
User::update(['name' => 'thinkphp', 'id' => 1]);
如果你需要只允许更新指定字段,可以使用
User::update(['name' => 'thinkphp', 'email' => 'thinkphp@qq.com'], ['id' => 1], ['name']);
上面的代码只会更新name字段的数据。
update源码:
/*** 更新数据* @access public* @param array $data 数据数组* @param mixed $where 更新条件* @param array $allowField 允许字段* @param string $suffix 数据表后缀* @return static*/
public static function update(array $data, $where = [], array $allowField = [], string $suffix = '')
{$model = new static();if (!empty($allowField)) {$model->allowField($allowField);}if (!empty($where)) {$model->setUpdateWhere($where);}if (!empty($suffix)) {$model->setSuffix($suffix);}$model->exists(true)->save($data);return $model;
}
update方法底层还是使用了save方法。
5.4 查询数据 find select 查询构造器
模型查询和数据库查询方法的区别主要在于,模型中的查询的数据在获取的时候会经过获取器的处理,以及更加对象化的获取方式。
模型查询除了使用自身的查询方法外,一样可以使用数据库的查询构造器,返回的都是模型对象实例。但如果直接调用查询对象的方法,IDE可能无法完成自动提示。
获取单个数据 find
find 方法返回值为当前模型对象。默认参数为null值,传入的话会视为主键条件。
find源码:
/*** 查找单条记录* @access public* @param mixed $data 查询数据* @return array|Model|null|static|mixed* @throws Exception* @throws ModelNotFoundException* @throws DataNotFoundException*/
public function find($data = null)
{if (!is_null($data)) {// AR模式分析主键条件$this->parsePkWhere($data);}if (empty($this->options['where']) && empty($this->options['order'])) {$result = [];} else {$result = $this->connection->find($this);}// 数据处理if (empty($result)) {return $this->resultToEmpty();}if (!empty($this->model)) {// 返回模型对象$this->resultToModel($result);} else {$this->result($result);}return $result;
}
获取单个数据的方法:
// 取出主键为1的数据
$user = User::find(1);
echo $user->name;// 使用查询构造器查询满足条件的数据
$user = User::where('name', 'thinkphp')->find();
echo $user->name;
模型使用find方法查询,如果数据不存在返回Null,否则返回当前模型的对象实例。
使用isEmpty方法来判断当前是否为一个空模型。
$user = User::where('name', 'thinkphp')->findOrEmpty();
if (!$user->isEmpty()) {echo $user->name;
}
如果是在模型内部获取数据,不要使用
$this->name的方式来获取数据,而是使用$this->getAttr('name')替代。
获取多个数据 select
select 可以查询多条数据,返回值为collection。参数默认不写为null值,给出后会视为主键条件。
select 源码:
/*** 查找记录* @access public* @param mixed $data 数据* @return Collection|array|static[]* @throws Exception* @throws ModelNotFoundException* @throws DataNotFoundException*/
public function select($data = null): Collection
{if (!is_null($data)) {// 主键条件分析$this->parsePkWhere($data);}$resultSet = $this->connection->select($this);// 返回结果处理if (!empty($this->options['fail']) && count($resultSet) == 0) {$this->throwNotFound();}// 数据列表读取后的处理if (!empty($this->model)) {// 生成模型对象$resultSet = $this->resultSetToModelCollection($resultSet);} else {$this->resultSet($resultSet);}return $resultSet;
}
例如,取出多个数据:
// 根据主键获取多个数据
$list = User::select([1,2,3]);
// 对数据集进行遍历操作
foreach($list as $key=>$user){echo $user->name;
}
使用查询构造器 (链式操作)
在模型中仍然可以调用数据库的链式操作和查询方法,可以充分利用数据库的查询构造器的优势。
例如:
User::where('id',10)->find();
User::where('status',1)->order('id desc')->select();
User::where('status',1)->limit(10)->select();
使用查询构造器直接使用静态方法调用即可,无需先实例化模型。
获取某个字段或者某个列的值:
// 获取某个用户的积分
User::where('id',10)->value('score');
// 获取某个列的所有值
User::where('status',1)->column('name');
// 以id为索引
User::where('status',1)->column('name','id');
value和column方法返回的不再是一个模型对象实例,而是纯粹的值或者某个列的数组。
