衡水的网站建设windows优化大师可以卸载吗
我们想要的是:允许多个线程同时读,但只要有一个线程在写,其他线程就必须等待。
ReadWriteLock
ReadWriteLock的作用:
- 只允许一个线程写入(其他线程既不能写入也不能读取);
- 没有写入时,多个线程允许同时读(提高性能)。
- 如何声明读写锁:
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock lock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();private final Lock readLock = lock.readLock();private final Lock writeLock = lock.writeLock();
运行下面的代码发现:
读写锁并发的时候,读的数据并不是写入的终态数据

package org.meituan.javalearn.thread;import lombok.SneakyThrows;import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock;/*** @projectName: codebetter* @package: org.meituan.javalearn.thread* @className: ReadWriteQueue* @author: fangjiayueyuan* @description: TODO* @date: 2023/5/8 下午10:01* @version: 1.0*/
public class ReadWriteQueue {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {LinkedList<Thread> threadPools = new LinkedList<Thread>();final ReadWriteTaskQueue taskQueue = new ReadWriteTaskQueue();for(int i=0;i<199995;i++){threadPools.add(new Thread(new Runnable() {@SneakyThrows@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(taskQueue.getTask());}}));}Thread addThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 1005; i++) {taskQueue.addTask("The"+i+"th task to be closed");}}});addThread.start(); // 读写锁无法进行wait和notify???for(Thread thread:threadPools){thread.start();}}
}
class ReadWriteTaskQueue{private final ReentrantReadWriteLock lock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();private final Lock readLock = lock.readLock();private final Lock writeLock = lock.writeLock();LinkedList<String> taskQueue = new LinkedList<String>();public void addTask(String task){writeLock.lock();try{taskQueue.add(task);}finally {writeLock.unlock();}}public Integer getTask() throws InterruptedException {readLock.lock();try{while(taskQueue.isEmpty()){return 0;}return taskQueue.size();}finally {readLock.unlock();}}}
最初,写了一个类:ReadWriteTaskQueue,如下所示。队列可以实现增加任务和读取任务并打印的功能。但实际上,这个类实际上两个功能都在写,不是读写锁的应用场景。
package org.meituan.javalearn.thread;
import lombok.SneakyThrows;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock;/*** @projectName: codebetter* @package: org.meituan.javalearn.thread* @className: ReadWriteQueue* @author: fangjiayueyuan* @description: TODO* @date: 2023/5/8 下午10:01* @version: 1.0*/
public class ReadWriteQueue {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {LinkedList<Thread> threadPools = new LinkedList<Thread>();final ReadWriteTaskQueue taskQueue = new ReadWriteTaskQueue();for(int i=0;i<15;i++){threadPools.add(new Thread(new Runnable() {@SneakyThrows@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(taskQueue.getTask());}}));}Thread addThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {taskQueue.addTask("The"+i+"th task to be closed");}}});addThread.start(); // 读写锁无法进行wait和notify???for(Thread thread:threadPools){thread.start();}}
}
class ReadWriteTaskQueue{private final ReentrantReadWriteLock lock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();private final Lock readLock = lock.readLock();private final Lock writeLock = lock.writeLock();LinkedList<String> taskQueue = new LinkedList<String>();public void addTask(String task){writeLock.lock();try{taskQueue.add(task);}finally {writeLock.unlock();}}public String getTask() throws InterruptedException {readLock.lock();try{while(taskQueue.isEmpty()){return "None";}return taskQueue.remove();}finally {readLock.unlock();}}
}
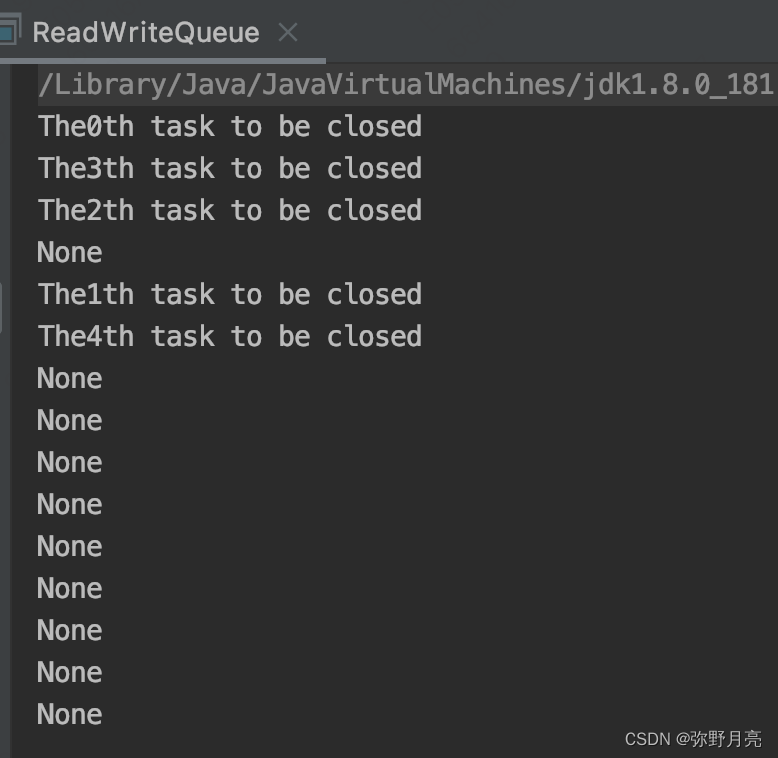
注意:ReadWriteLock看起来无法实现线程的协调,如果需要做类似于发布-订阅这种模式的消息队列,则需要通过Condition实现wait和notify来达到多线程协调的目的。
总结:
- 使用ReadWriteLock可以提高读取效率:
– ReadWriteLock只允许一个线程写入;
– ReadWriteLock允许多个线程在没有写入时同时读取;
– ReadWriteLock适合读多写少的场景。 - 缺点:
如果有线程正在读,写线程需要等待读线程释放锁后才能获取写锁,即读的过程中不允许写,这是一种悲观的读锁。
StampedLock
乐观锁的意思就是乐观地估计读的过程中大概率不会有写入,因此被称为乐观锁。悲观锁就是在读的过程中拒绝写入,显然乐观锁的并发效率更高。但有可能造成读写不一致。因此需要增加一些代码来判断读的状态。
声明StampedLock:private final StampedLock lock = new StampedLock;
读锁,需要判断读的时候有没有写入,通过盖得“章”Stamp来判断:
long stamp = lock.tryOptimisticRead();// 先尝试使用乐观锁
if(!validate(stamp)) // 通过Stamp来判断,顾名思义StampedLock 已经盖过章的lock
stamp = lock.readLock(); // 如果在读的时候进行了写入,则需要悲观锁来读一遍 由于大概率读的时候不会写,所以大概率都是走的乐观锁,因此能提高并发
lock.unlockRead(stamp);// 记得关闭读锁
写锁:
long stamp = lock.writeLock(); // 上写锁
lock.unlockWrite(stamp); // 关闭写锁
使用StampedLock对上面的ReadWriteTaskQueue进行改造如下:
class ReadWriteTaskQueue{private final StampedLock lock = new StampedLock();LinkedList<String> taskQueue = new LinkedList<String>();public void addTask(String task){ // 写锁long stamp = lock.writeLock();try{taskQueue.add(task);}finally {lock.unlockWrite(stamp);}}public Integer getTask() throws InterruptedException {long stamp = lock.tryOptimisticRead();if(!lock.validate(stamp)){try{stamp = lock.readLock();while(taskQueue.isEmpty()){return 0;}return taskQueue.size();}finally {lock.unlockRead(stamp);}}return taskQueue.size();}
}