望城区建设局网站seo搜索引擎优化培训班
目录
- 进程的诞生
- fork函数
- fork的本质
- fork的常规用法
- fork调用失败的原因
- 进程的死亡
- 进程退出的场景
- 常见的进程退出方法
- 正常终止(代码跑完)
- echo $?
- main函数返回
- 调用exit
- 调用_exit
- exit和_exit的区别
- 进程等待
- 进程等待的重要性
- 进程等待的函数
- wait
- waitpid
- 进程退出信息——status
- status是什么
- status怎么用
- Linux源码中的退出码对照表
- 进程程序替换
- 替换原理
- 替换函数
- execl
- execv
- execlp
- execvp
- execle
- execve
- 50行代码实现小型shell
- 获取命令行
- 解析命令
- 创建子进程(fork)
- 子进程进行程序替换(exec系列函数)
- 父进程等待子进程(waitpid)
- 代码
进程的诞生
fork函数
- 在Linux中,进程用来创建子进程的函数就是fork。
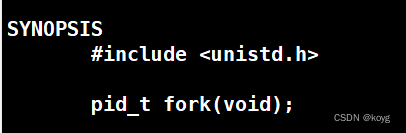
函数返回值为:
- 子进程返回0。
- 父进程返回子进程pid(父进程可能有多个子进程,父进程通过fork返回子进程pid区分各个子进程)。
- 出错比如创建进程失败返回-1。
在进程概念这一片文章中我们已经使用过fork函数,接下来,我们来了解一下fork函数到底做了一些什么。
fork的本质
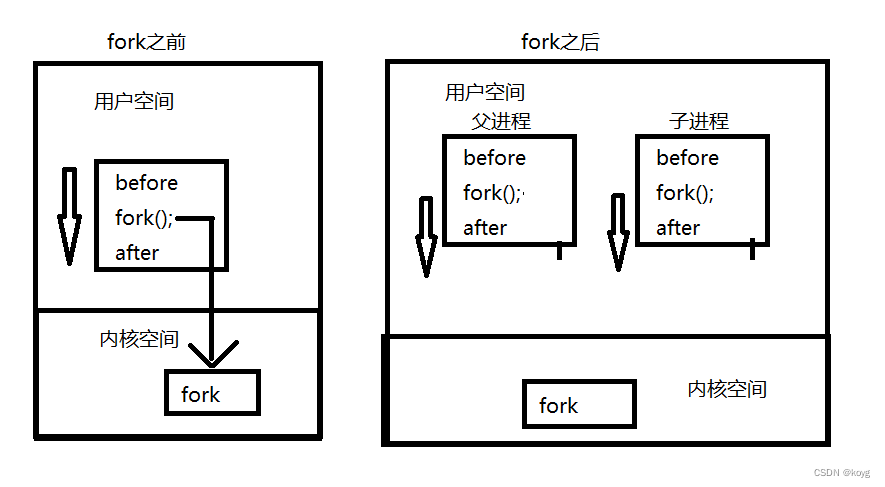
- 我们知道fork创建进程后会有两个执行流,但是不要认为这两个执行流实在fork完成后产生的,其实它们在fork内部就已经产生了,这就是为什么fork有两个返回值的原因。
我们来了解一下fork到底做了一些什么。
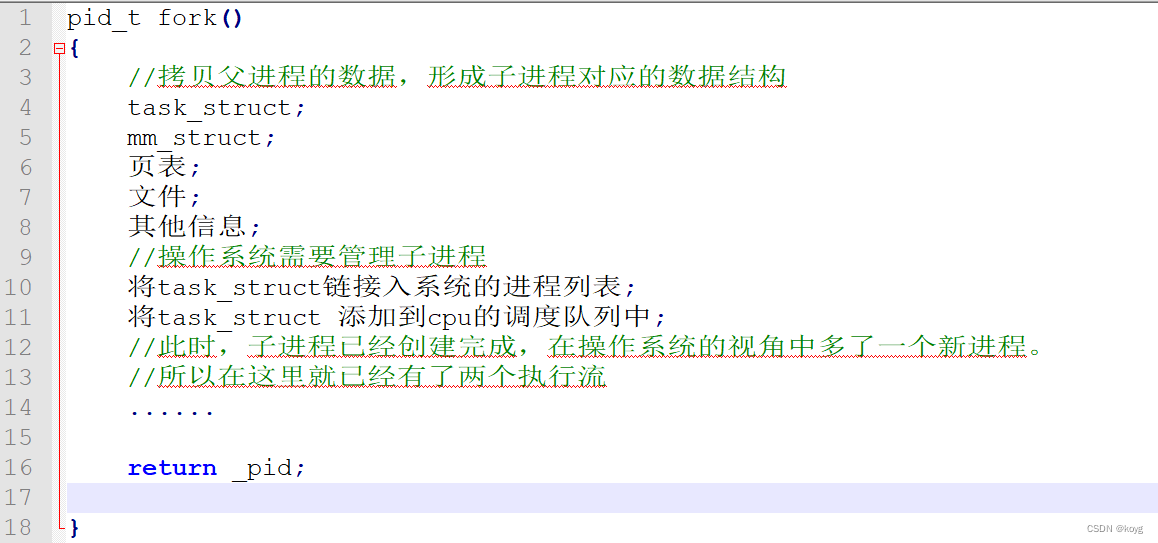
- 我们知道操作系统通过管理相关结构体管理进程,所以创建一个进程其实就是创建并填充task_struct,mm_struct,页表等相关结构体,所以fork第一步就是向内存申请一块空间,然后创建相关结构体并且拷贝父进程的数据。
- 在创建相关结构体后,操作系统会将子进程添加到系统进程列表中即将这些结构体链接到相关数据结构中,比如将task_struct链接到cpu的调度队列中等等,在上述操作完成后,进程就已经创建完成,此时,就多了一个执行流。
fork的常规用法
- 使用if判断语句通过fork的返回值进行分流
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>int main()
{pid_t pid=fork();if(pid > 0){//father do something...}else if(pid == 0){//child do something...}return 0;
}
- 通过exec函数进行程序替换,可以实现一个进程执行另一个程序的代码。(后面细嗦)
fork调用失败的原因
- 系统中进程太多导致内存不足。
- 用户的进程数超过系统限制。
进程的死亡
进程退出的场景
- 代码跑完结果正确。
- 代码跑完结果不正确。
- 进程异常退出(发生除0、栈溢出、野指针、越界访问等等)。
任何进程退出的情况都属于上面几种。
常见的进程退出方法
正常终止(代码跑完)
echo $?
查看最近的进程退出码
main函数返回
这个方式是我们最为熟悉的,在我们写C\C++代码时最后写的**“return n;”就是所谓的main函数返回**。
main函数中,return操作过后,返回值会当作exit的参数。
注意:只有main函数中的return具有退出进程的作用,main函数是程序的入口,return只是将返回值传给调用函数,并不能在main函数调用的函数退出进程。
比如下面add函数的return时,只是返回main函数调用add函数的地方,所以return的作用严谨的讲是结束当前函数,将返回值穿给调用函数。,
#include<stdio.h>int add(int a, int b)
{return a+b;
}int main()
{int a=10;int b=20;int ret=add(a,b);return ret;
}
调用exit
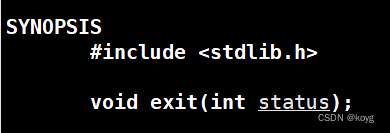
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>int add(int a, int b)
{exit(1);return a+b;
}int main()
{int a=10;int b=20;int ret=add(a,b);return 0;
}
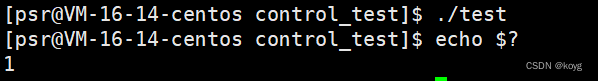
我们可以从结果看出进程确实是在add函数中退出,说明exit可以在任意位置结束进程。
调用_exit
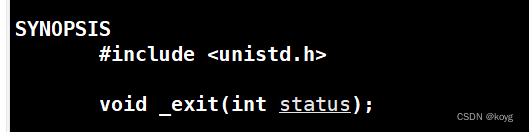
在用法上与exit一致,那我们来聊聊_exit和exit的区别。
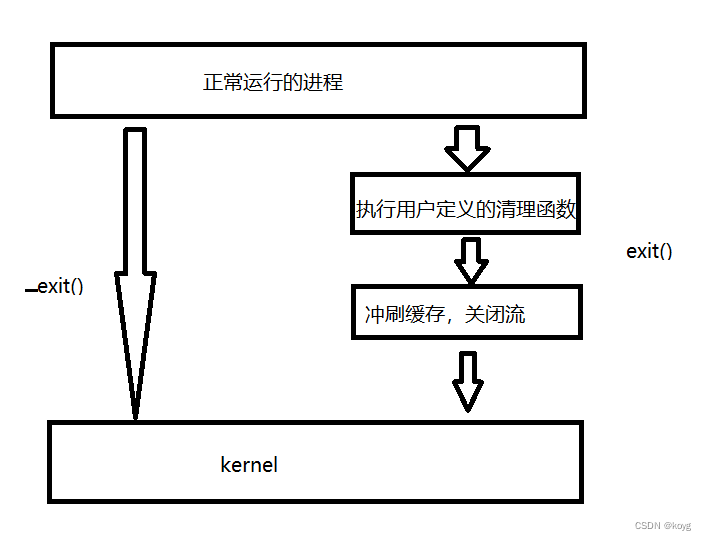
exit和_exit的区别
- exit会在退出进程前执行用户定义的清理函数。
- exit会冲刷缓存(将缓存区中的数据刷新),关闭流(c语言中默认打开的标准输入流、标准输出流、标准错误流)。
- exit最后会调用_exit。
进程等待
进程等待的重要性
- 在进程概念中讲过僵尸进程,当子进程退出,父进程如果一直不去读取子进程的退出信息时,子进程会变成僵尸进程,从而导致内存泄漏。
- 僵尸进程一旦形成,kill也没办法。
- 父进程把任务派发给子进程,父进程应关心子进程的完成情况:任务是否正确完成,子进程是否异常退出。
- 父进程通过进程等待的方式,回收子进程资源,读取子进程退出信息。
进程等待的函数
wait
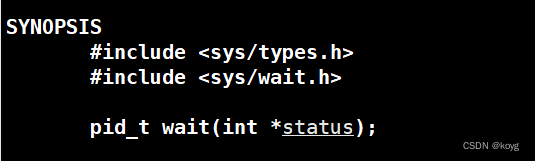
- 返回值:若等待成功返回等待进程的pid,失败则返回-1。
- 参数:输出型参数,用于获取进程的退出信息,不关心则传NULL。
我们通过一段代码了解他的使用方式。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>int main()
{pid_t pid=fork();if(pid == 0){//childsleep(5);exit(0);}else if(pid > 0){pid_t ret_id=wait(NULL);if(pid == ret_id){printf("pid == ret_id\n");}else{printf("error!!!\n");}}else{printf("fork error!!!\n");}return 0;
}
因为子进程sleep了5秒,父进程没有,父进程应该退出,子进程变成僵尸进程。

但是我们可以看到父进程明明没有sleep但是它的STAT和子进程都是S,说明wait是阻塞式等待。
waitpid
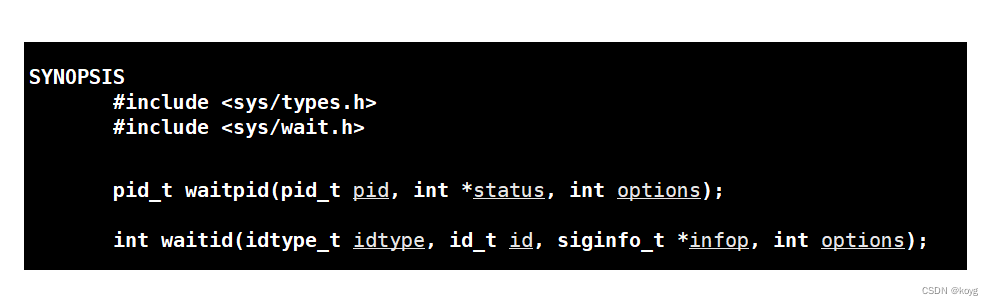
返回值:
- 等待成功则返回等待进程pid
- 如果设置了选项WNOHANG,而调用waitpid发现没有已退出的子进程则返回0。
- 调用出现错误则返回-1,且error会被设置成相应的值。
pid:
- pid=-1时,父进程等待任一子进程,效果与wait相同
- pid>0时,父进程等待指定pid的子进程。
status:
- 输出型参数,进程退出信息。
options:
- 选项WNOHANG,若等待进程没有结束则返回0继续跑自己的代码,当等待正常结束的子进程时,返回子进程pid。
现在我们先不关心进程的退出信息,先实现一下回收多个子进程。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>int main()
{int pid_array[5]={0};int i=0;while(i < 5){pid_array[i]=fork();if(pid_array[i] == 0){//childprintf("child do something...\n");exit(0);}else if(pid_array[i] > 0){//father}else{printf("fork error!!!\n");}i++;}sleep(5);i=0;while(i < 5){pid_t pid = waitpid(pid_array[i],NULL,0);if(pid == pid_array[i]){printf("pid == ret_id\n");}else{printf("error!!!\n");}sleep(1);i++;}return 0;
}
进程退出信息——status
status是什么
- 我们知道wait和waitpid都有一个参数叫做status,这个参数是父进程用于获取子进程退出信息,是输出性参数,由操作系统填充。
- 如果传入NULL,表示不关心退出信息
- status不能简单地看成一个整形,可以看待成一个位图。
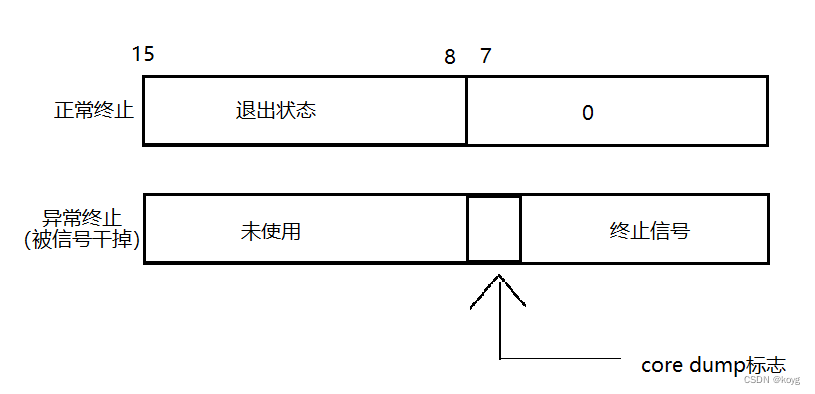
我们知道在进程退出时,情况分为:
- 进程正常退出(通过查看退出状态判断结果是否正确)
- 进程异常终止(退出状态无意义)
status怎么用
- 可以通过位操作获得退出信息。(此方法麻烦,不推荐)
- 可以通过相关宏获得退出信息
WIFEXITED(status): 若为正常终止子进程返回的状态,则为真。(查看进程是否是正常退出)
WEXITSTATUS(status): 若WIFEXITED非零,提取子进程退出码。(查看进程的退出码)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>int main()
{pid_t pid=fork();if(pid == 0){//childsleep(5);exit(0);}else if(pid > 0){int status=0;pid_t ret_id=waitpid(pid,&status,0);if(WIFEXITED(status)){printf("exit_code:%d\n",WEXITSTATUS(status));}else{printf("error!!!\n");}}else{printf("fork error!!!\n");}return 0;
}

关于退出码:其实我们并不擅长处理数据信息,我们更加擅长出来字符串信息,所以在获得退出码后我们往往需要在退出码对照表中找到相应信息。
Linux源码中的退出码对照表
路径:/include/asm-generic/errno-base.h链接
#ifndef _ASM_GENERIC_ERRNO_BASE_H
#define _ASM_GENERIC_ERRNO_BASE_H#define EPERM 1 /* Operation not permitted */
#define ENOENT 2 /* No such file or directory */
#define ESRCH 3 /* No such process */
#define EINTR 4 /* Interrupted system call */
#define EIO 5 /* I/O error */
#define ENXIO 6 /* No such device or address */
#define E2BIG 7 /* Argument list too long */
#define ENOEXEC 8 /* Exec format error */
#define EBADF 9 /* Bad file number */
#define ECHILD 10 /* No child processes */
#define EAGAIN 11 /* Try again */
#define ENOMEM 12 /* Out of memory */
#define EACCES 13 /* Permission denied */
#define EFAULT 14 /* Bad address */
#define ENOTBLK 15 /* Block device required */
#define EBUSY 16 /* Device or resource busy */
#define EEXIST 17 /* File exists */
#define EXDEV 18 /* Cross-device link */
#define ENODEV 19 /* No such device */
#define ENOTDIR 20 /* Not a directory */
#define EISDIR 21 /* Is a directory */
#define EINVAL 22 /* Invalid argument */
#define ENFILE 23 /* File table overflow */
#define EMFILE 24 /* Too many open files */
#define ENOTTY 25 /* Not a typewriter */
#define ETXTBSY 26 /* Text file busy */
#define EFBIG 27 /* File too large */
#define ENOSPC 28 /* No space left on device */
#define ESPIPE 29 /* Illegal seek */
#define EROFS 30 /* Read-only file system */
#define EMLINK 31 /* Too many links */
#define EPIPE 32 /* Broken pipe */
#define EDOM 33 /* Math argument out of domain of func */
#define ERANGE 34 /* Math result not representable */#endif
路径:/include/asm-generic/errno.h链接
#ifndef _ASM_GENERIC_ERRNO_H
#define _ASM_GENERIC_ERRNO_H#include <asm-generic/errno-base.h>#define EDEADLK 35 /* Resource deadlock would occur */
#define ENAMETOOLONG 36 /* File name too long */
#define ENOLCK 37 /* No record locks available */
#define ENOSYS 38 /* Function not implemented */
#define ENOTEMPTY 39 /* Directory not empty */
#define ELOOP 40 /* Too many symbolic links encountered */
#define EWOULDBLOCK EAGAIN /* Operation would block */
#define ENOMSG 42 /* No message of desired type */
#define EIDRM 43 /* Identifier removed */
#define ECHRNG 44 /* Channel number out of range */
#define EL2NSYNC 45 /* Level 2 not synchronized */
#define EL3HLT 46 /* Level 3 halted */
#define EL3RST 47 /* Level 3 reset */
#define ELNRNG 48 /* Link number out of range */
#define EUNATCH 49 /* Protocol driver not attached */
#define ENOCSI 50 /* No CSI structure available */
#define EL2HLT 51 /* Level 2 halted */
#define EBADE 52 /* Invalid exchange */
#define EBADR 53 /* Invalid request descriptor */
#define EXFULL 54 /* Exchange full */
#define ENOANO 55 /* No anode */
#define EBADRQC 56 /* Invalid request code */
#define EBADSLT 57 /* Invalid slot */#define EDEADLOCK EDEADLK#define EBFONT 59 /* Bad font file format */
#define ENOSTR 60 /* Device not a stream */
#define ENODATA 61 /* No data available */
#define ETIME 62 /* Timer expired */
#define ENOSR 63 /* Out of streams resources */
#define ENONET 64 /* Machine is not on the network */
#define ENOPKG 65 /* Package not installed */
#define EREMOTE 66 /* Object is remote */
#define ENOLINK 67 /* Link has been severed */
#define EADV 68 /* Advertise error */
#define ESRMNT 69 /* Srmount error */
#define ECOMM 70 /* Communication error on send */
#define EPROTO 71 /* Protocol error */
#define EMULTIHOP 72 /* Multihop attempted */
#define EDOTDOT 73 /* RFS specific error */
#define EBADMSG 74 /* Not a data message */
#define EOVERFLOW 75 /* Value too large for defined data type */
#define ENOTUNIQ 76 /* Name not unique on network */
#define EBADFD 77 /* File descriptor in bad state */
#define EREMCHG 78 /* Remote address changed */
#define ELIBACC 79 /* Can not access a needed shared library */
#define ELIBBAD 80 /* Accessing a corrupted shared library */
#define ELIBSCN 81 /* .lib section in a.out corrupted */
#define ELIBMAX 82 /* Attempting to link in too many shared libraries */
#define ELIBEXEC 83 /* Cannot exec a shared library directly */
#define EILSEQ 84 /* Illegal byte sequence */
#define ERESTART 85 /* Interrupted system call should be restarted */
#define ESTRPIPE 86 /* Streams pipe error */
#define EUSERS 87 /* Too many users */
#define ENOTSOCK 88 /* Socket operation on non-socket */
#define EDESTADDRREQ 89 /* Destination address required */
#define EMSGSIZE 90 /* Message too long */
#define EPROTOTYPE 91 /* Protocol wrong type for socket */
#define ENOPROTOOPT 92 /* Protocol not available */
#define EPROTONOSUPPORT 93 /* Protocol not supported */
#define ESOCKTNOSUPPORT 94 /* Socket type not supported */
#define EOPNOTSUPP 95 /* Operation not supported on transport endpoint */
#define EPFNOSUPPORT 96 /* Protocol family not supported */
#define EAFNOSUPPORT 97 /* Address family not supported by protocol */
#define EADDRINUSE 98 /* Address already in use */
#define EADDRNOTAVAIL 99 /* Cannot assign requested address */
#define ENETDOWN 100 /* Network is down */
#define ENETUNREACH 101 /* Network is unreachable */
#define ENETRESET 102 /* Network dropped connection because of reset */
#define ECONNABORTED 103 /* Software caused connection abort */
#define ECONNRESET 104 /* Connection reset by peer */
#define ENOBUFS 105 /* No buffer space available */
#define EISCONN 106 /* Transport endpoint is already connected */
#define ENOTCONN 107 /* Transport endpoint is not connected */
#define ESHUTDOWN 108 /* Cannot send after transport endpoint shutdown */
#define ETOOMANYREFS 109 /* Too many references: cannot splice */
#define ETIMEDOUT 110 /* Connection timed out */
#define ECONNREFUSED 111 /* Connection refused */
#define EHOSTDOWN 112 /* Host is down */
#define EHOSTUNREACH 113 /* No route to host */
#define EALREADY 114 /* Operation already in progress */
#define EINPROGRESS 115 /* Operation now in progress */
#define ESTALE 116 /* Stale NFS file handle */
#define EUCLEAN 117 /* Structure needs cleaning */
#define ENOTNAM 118 /* Not a XENIX named type file */
#define ENAVAIL 119 /* No XENIX semaphores available */
#define EISNAM 120 /* Is a named type file */
#define EREMOTEIO 121 /* Remote I/O error */
#define EDQUOT 122 /* Quota exceeded */#define ENOMEDIUM 123 /* No medium found */
#define EMEDIUMTYPE 124 /* Wrong medium type */
#define ECANCELED 125 /* Operation Canceled */
#define ENOKEY 126 /* Required key not available */
#define EKEYEXPIRED 127 /* Key has expired */
#define EKEYREVOKED 128 /* Key has been revoked */
#define EKEYREJECTED 129 /* Key was rejected by service *//* for robust mutexes */
#define EOWNERDEAD 130 /* Owner died */
#define ENOTRECOVERABLE 131 /* State not recoverable */#define ERFKILL 132 /* Operation not possible due to RF-kill */#define EHWPOISON 133 /* Memory page has hardware error */#endif
进程程序替换
替换原理
进程用fork创建子进程(其代码和数据拷贝至父进程),虽说可以用条件语句分流,但是这样使用并不方便,我们往往让子进程调用exec系列函数实现程序替换,当进程调用exec系列函数时,代码和数据会被磁盘中的可执行程序完全覆盖,从而实现进程程序替换。但是注意exec系列函数并不是创建新的进程,而是将调用进程的代码和数据进行替换。
替换函数
exec系列函数(不同后缀不同用法)的头文件为unistd.h
execl
int execl(const char *path, const char *arg, …);
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>int main()
{pid_t pid=fork();if(pid == 0){//childexecl("/usr/bin/ls","ls","-a","-l",NULL); //将子进程替换成ls}else if(pid > 0){//fatherpid_t pid=wait(NULL);if(pid > 0){printf("wait child success\n");}else{printf("wait error\n");exit(1);}}return 0;
}
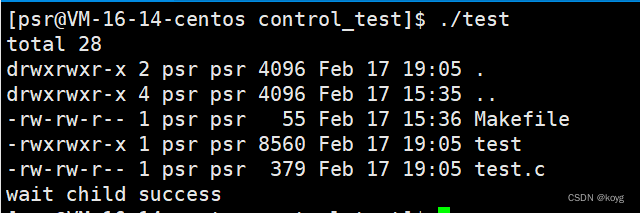
l后缀代表以可变参数列表的方式传参,以NULL结束。
execv
int execv(const char *path, char *const argv[]);
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>int main()
{pid_t pid=fork();if(pid == 0){//childchar* arg[]={"ls","-a","-l"};execv("/usr/bin/ls",arg);}else if(pid > 0){//fatherpid_t pid=wait(NULL);if(pid > 0){printf("wait child success\n");}else{printf("wait error\n");exit(1);}}return 0;
}
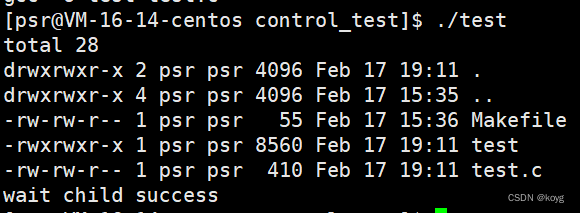
v后缀代表通过数组方式传参。
execlp
int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, …);
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>int main()
{pid_t pid=fork();if(pid == 0){//childexeclp("ls","ls","-a","-l",NULL);}else if(pid > 0){//fatherpid_t pid=wait(NULL);if(pid > 0){printf("wait child success\n");}else{printf("wait error\n");exit(1);}}return 0;
}
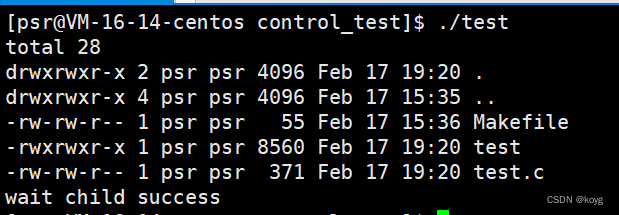
p后缀代表自动搜索环境变量PATH,替换的可执行程序可以不带路径。
注意带l后缀的请务必在传参时用NULL结束。
execvp
int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>int main()
{pid_t pid=fork();if(pid == 0){//childchar* arg[]={"ls","-a","-l"};execvp("ls",arg);}else if(pid > 0){//fatherpid_t pid=wait(NULL);if(pid > 0){printf("wait child success\n");}else{printf("wait error\n");exit(1);}}return 0;
}
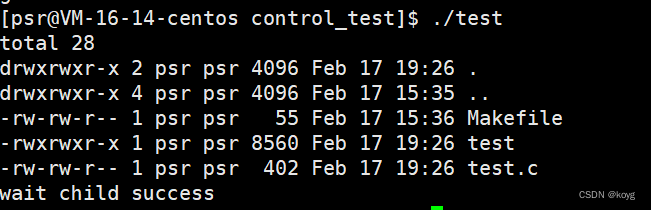
execle
int execle(const char *path, const char *arg, …,char *const envp[]);
test.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>int main()
{pid_t pid=fork();if(pid == 0){//childchar* envp[]={"PATH=/bin:/usr/bin"};execle("my_printf","my_printf","-a","-b",NULL,envp);}else if(pid > 0){//fatherpid_t pid=wait(NULL);if(pid > 0){printf("wait child success\n");}else{printf("wait error\n");exit(1);}}return 0;
}my_pritnf.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>int main(int argc,char* argv[],char* env[])
{int i=0;for(; i<argc; i++){printf("argv[i]:%s\n",argv[i]);}printf("PATH:%s\n",getenv("PATH"));return 0;
}
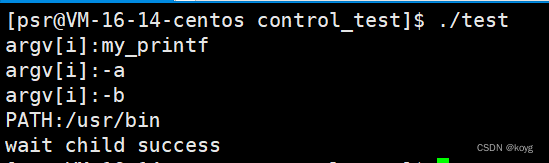
我们在环境变量中了解到main函数的第三个变量是环境变量,e后缀代表自己传环境变量。
execve
int execve(const char *path, char *const argv[], char *const envp[]);
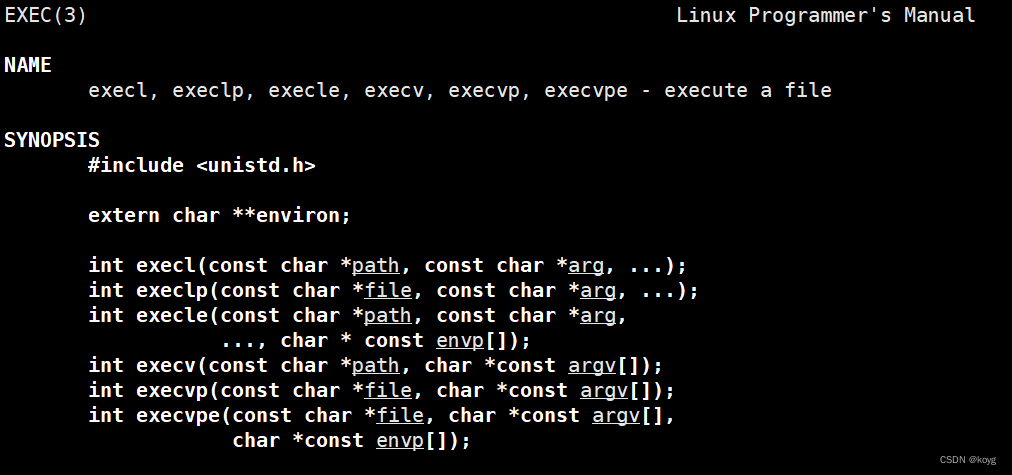
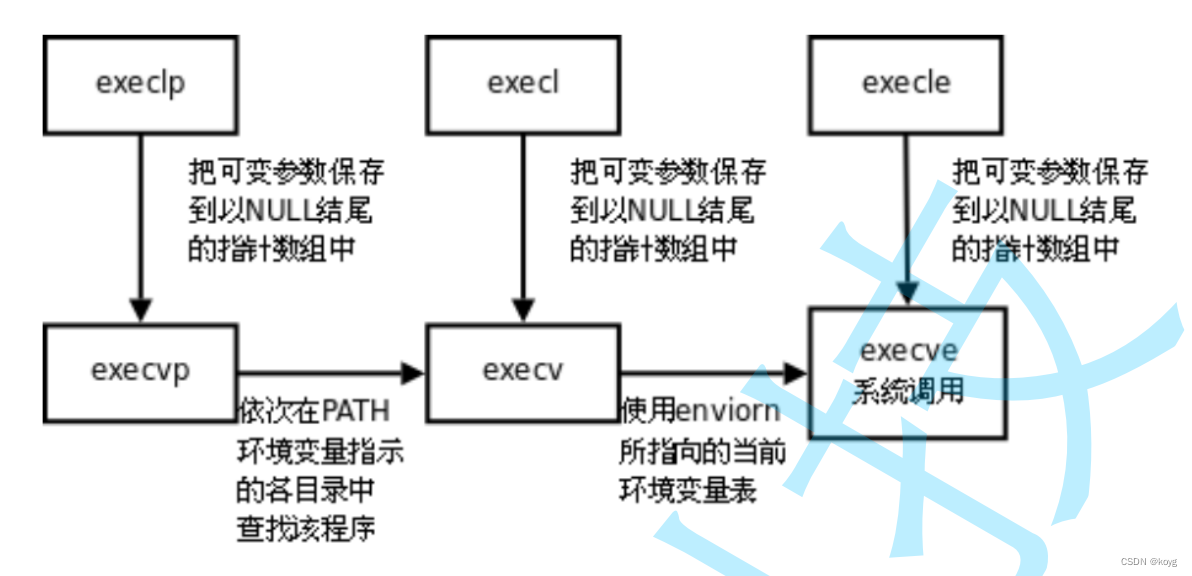
我们可以看到exec系列函数中除了execve,其他函数都在一个文件中,这是因为execve是系统调用接口,其他的都是经过封装后方便我们使用的函数,它们底层都是调用的execve函数。
50行代码实现小型shell
我们先想想shell的运行过程:
- 读取命令
- bash创建子进程执行命令,bash阻塞等待
- 重复上述过程
所以我们的shell的运行逻辑是:
获取命令行
向标准输入流中读取命令
fgets(cmd, LEN, stdin);
解析命令
使用strtok函数以空格为分隔符,将读取的命令字符串截取为一个个选项方便给execvp传参。
cmd[strlen(cmd)-1] = '\0';myarg[0] = strtok(cmd, " ");int i = 1;while(myarg[i] = strtok(NULL, " ")){i++;}
创建子进程(fork)
pid_t id = fork();
子进程进行程序替换(exec系列函数)
if(id == 0){//childexecvp(myarg[0], myarg);exit(11);}
父进程等待子进程(waitpid)
int status = 0;pid_t ret = waitpid(id, &status, 0);if(WIFEXITED(status)){printf("exit code: %d\n", WEXITSTATUS(status));}
代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>#define LEN 1024
#define NUM 32int main()
{char cmd[LEN];char *myarg[NUM];while(1){printf("[psr@my-centos_mc dir]# ");fgets(cmd, LEN, stdin);cmd[strlen(cmd)-1] = '\0';myarg[0] = strtok(cmd, " ");int i = 1;while(myarg[i] = strtok(NULL, " ")){i++;}//printf("%s", cmd);pid_t id = fork();if(id == 0){//childexecvp(myarg[0], myarg);exit(11);}int status = 0;pid_t ret = waitpid(id, &status, 0);if(WIFEXITED(status)){printf("exit code: %d\n", WEXITSTATUS(status));}else{exit(1);}}return 0;
}
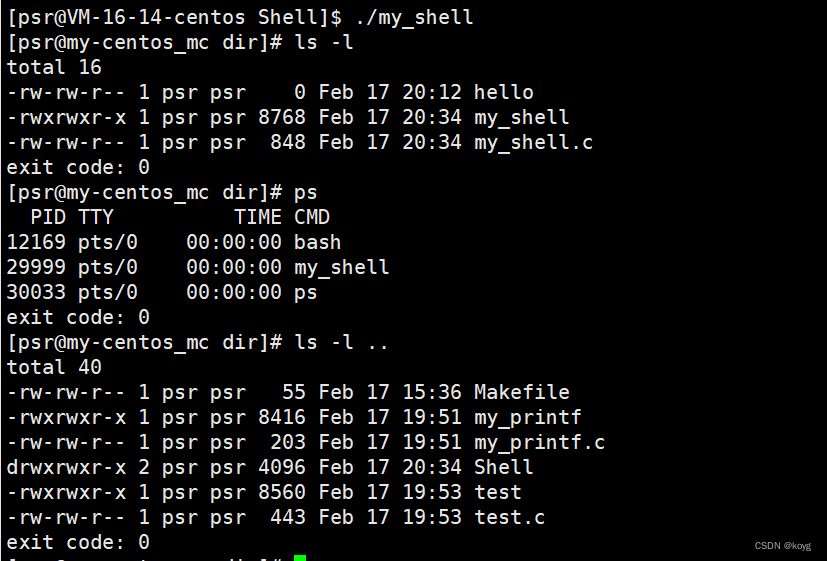
虽然这个shell的功能单一并且涉及到管道等等的命令不能实现,但是小型shell的实现有利于我们理解本篇博客的内容。
