网站建设图片如何优化做广告的软件app免费
1 扩展运算符
扩展运算符(spread)是三个点(…). 它好比 rest 参数的逆运算,将一个数组转为用逗号分隔的参数序列.
console.log(...[1, 2, 3]) // 1 2 3console.log(1, ...[2, 3, 4], 5) // 1 2 3 4 5
该运算符主要用于函数调用
<script>function push(array, ...items) {array.push(...items);}function add(x, y) {return x + y;}const numbers = [4, 38];console.log(add(...numbers)); // 42let arrayNumber = []push(arrayNumber, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5)console.log(arrayNumber); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
</script>
上面代码中,array.push(…items)和add(…numbers)这两行,都是函数的调用,它们都使用了扩展运算符. 该运算符将一个数组,变为参数序列.
扩展运算符与正常的函数参数可以结合使用,非常灵活.
<script>function f(a, b, c, d, e) {console.log(a, b, c, d, e) // -1 0 1 2 3}const args = [0, 1];f(-1, ...args, 2, ...[3]);
</script>
扩展运算符后面还可以放置表达式.
<script>const x = 1const arr = [...(x > 0 ? [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] : []),'b',];console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 'b']
</script>
2 替代函数的 apply 方法
由于扩展运算符可以展开数组,所以不再需要apply方法,将数组转为函数的参数了.
<script>// ES6的写法function f(x, y, z) {console.log(x, y, z) // 0 1 2}let args = [0, 1, 2];f(...args);
</script>
下面是扩展运算符取代apply方法的一个实际的栗子,应用Math.max方法,简化求出一个数组最大元素的写法.
<script>// ES6 的写法console.log(Math.max(...[14, 3, 77]));// 等同于console.log(Math.max(14, 3, 77));
</script>
另一个栗子是通过push函数,将一个数组添加到另一个数组的尾部.
<script>// ES6 的写法let arr1 = [0, 1, 2];let arr2 = [3, 4, 5];arr1.push(...arr2);console.log(arr1); // [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]console.log(arr2); // [3, 4, 5]
</script>
3 扩展运算符的应用
数组是复合的数据类型,直接复制的话,只是复制了指向底层数据结构的指针,而不是克隆一个全新的数组 [ 浅拷贝].
<script>const a1 = [1, 2];const a2 = a1;a2[0] = 2;console.log(a1); // [2, 2]
</script>
上面代码中,a2并不是a1的克隆,而是指向同一份数据的另一个指针. 修改a2,会直接导致a1的变化.
ES5 只能用变通方法来复制数组.
<script>const a1 = [1, 2];const a2 = a1.concat();a2[0] = 2;console.log(a1); // [1, 2]
</script>
上面代码中,a1会返回原数组的克隆,再修改a2就不会对a1产生影响.
扩展运算符提供了复制数组的简便写法. -->这样就不会造成影响
<script>const a1 = [1, 2]const a2 = [...a1]a1[0] = 2console.log(a2); // [1, 2]
</script>
扩展运算符提供了数组合并的新写法.
<script>const arr1 = ['a', 'b'];const arr2 = ['c'];const arr3 = ['d', 'e'];// ES5 的合并数组arr1.concat(arr2, arr3);// [ 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e' ]// ES6 的合并数组[...arr1, ...arr2, ...arr3]// [ 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e' ]
</script>
不过,这两种方法都是浅拷贝 ( 指的是内部数据如 { foo: 1 } 是存地址 ) ,使用的时候需要注意.
<script>const a1 = [{foo: 1}];const a2 = [{bar: 2}];const a3 = a1.concat(a2);const a4 = [...a1, ...a2];console.log(a3);console.log(a4);console.log(a3[0] === a1[0]); // trueconsole.log(a4[0] === a1[0]); // trueconsole.log(a3[0] === a4[0]); // truea3[0].foo = 2console.log(a3);console.log(a4);</script>
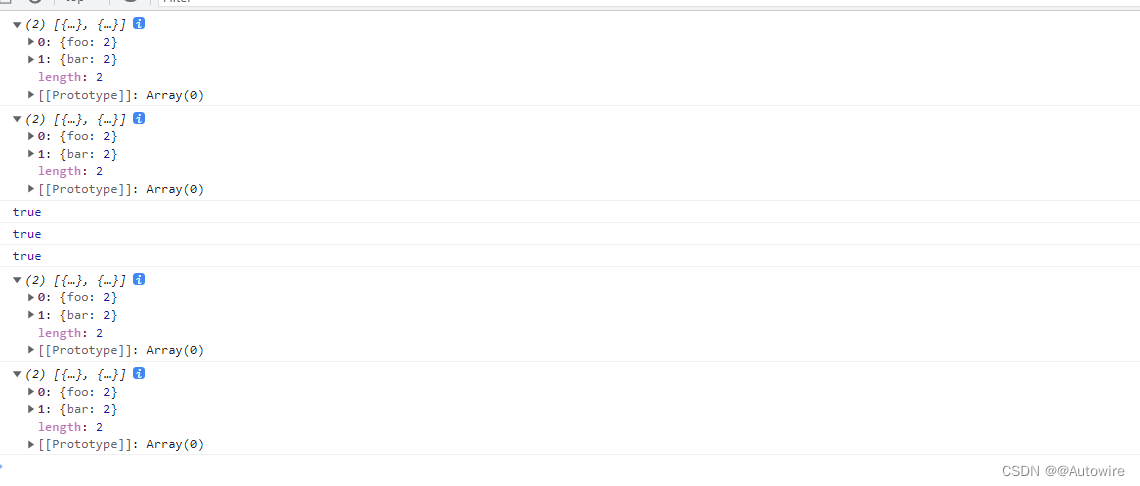
上面代码中,[ a3 ] 和 [ a4 ] 是用两种不同方法合并而成的新数组,但是它们的成员都是对原数组成员的引用,这就是浅拷贝. 如果修改了引用指向的值,会同步反映到新数组.
扩展运算符可以与解构赋值结合起来,用于生成数组.
<script>let list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]let a = list[0]let rest = list.splice(1)console.log(a) // 1console.log(rest) // [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]let listNew = [a, ...rest]console.log(listNew); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]</script>
<script>const [first, ...rest] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];//first == 1//rest == [2, 3, 4, 5]const [first, ...rest] = [];//first == undefined//rest == []const [first, ...rest] = ["foo"];//first == "foo"//rest == []
</script>
如果将扩展运算符用于数组赋值,只能放在参数的最后一位,否则会报错.
const [...butLast, last] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
// 报错const [first, ...middle, last] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
// 报错
扩展运算符还可以将字符串转为真正的数组.
<script>let newVar = [...'hello'];console.log(newVar); // ['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o']
</script>
任何定义了遍历器(Iterator)接口的对象,都可以用扩展运算符转为真正的数组.
let nodeList = document.querySelectorAll('div');
let array = [...nodeList];
上面代码中,querySelectorAll方法返回的是一个NodeList对象. 它不是数组,而是一个类似数组的对象. 这时,扩展运算符可以将其转为真正的数组,原因就在于NodeList对象实现了 Iterator .
对于那些没有部署 Iterator 接口的类似数组的对象,扩展运算符就无法将其转为真正的数组.
<script>let arrayLike = {'0': 'a','1': 'b','2': 'c',};// TypeError: Cannot spread non-iterable object.let arr = [...arrayLike];console.log(arr);
</script>
上面代码中,arrayLike是一个类似数组的对象,但是没有部署 Iterator 接口,扩展运算符就会报错. 这时,可以改为使用Array.from方法将arrayLike转为真正的数组.
扩展运算符内部调用的是数据结构的 Iterator 接口,因此只要具有 Iterator 接口的对象,都可以使用扩展运算符,比如 Map 结构.
<script>let map = new Map([[1, 'one'],[2, 'two'],[3, 'three']]);let newVar = [...map];console.log(newVar);
</script>
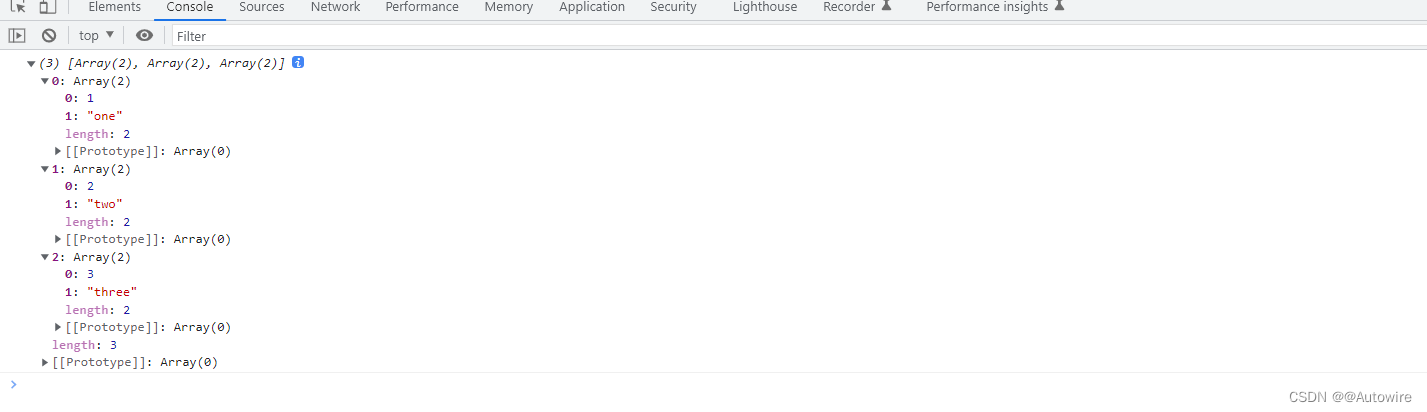
<script>let map = new Map([[1, 'one'],[2, 'two'],[3, 'three']]);console.log(...map.keys());console.log(...map.values());// 1 2 3// one two three
</script>
4 Array.from()
Array.from方法用于将两类对象转为真正的数组: 类似数组的对象(array-like object)和可遍历(iterable)的对象(包括 ES6 新增的数据结构 Set 和 Map).
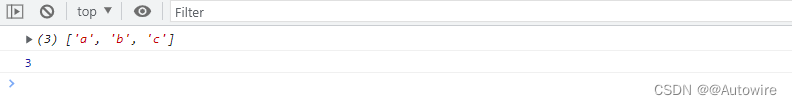
下面是一个类似数组的对象,Array.from将它转为真正的数组.
<script>let arrayLike = {'0': 'a','1': 'b','2': 'c',length: 3};// ES6的写法 T[]let arr2 = Array.from(arrayLike); // ['a', 'b', 'c']console.log(arr2);console.log(arr2.length);
</script>
实际应用中,常见的类似数组的对象是 DOM 操作返回的 NodeList 集合,以及函数内部的arguments对象. Array.from都可以将它们转为真正的数组.
<script>// NodeList对象let ps = document.querySelectorAll('p');let psNew = Array.from(ps).filter(p => {return p.textContent.length > 4;});console.log(psNew);// arguments对象function foo() {return Array.from(arguments);}let arrNew = foo(1,2,3,4,5,6)console.log(arrNew);
</script>
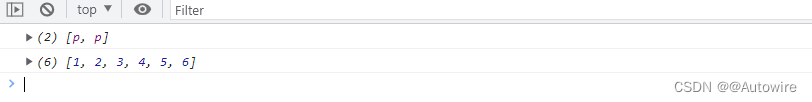
上面代码中,querySelectorAll方法返回的是一个类似数组的对象,可以将这个对象转为真正的数组,再使用filter方法.
只要是部署了 Iterator 接口的数据结构,Array.from都能将其转为数组.
Array.from('hello')
// ['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o']let namesSet = new Set(['a', 'b'])
Array.from(namesSet) // ['a', 'b']
上面代码中,字符串和 Set 结构都具有 Iterator 接口,因此可以被Array.from转为真正的数组.
如果参数是一个真正的数组,Array.from会返回一个一模一样的新数组.
Array.from([1, 2, 3])
// [1, 2, 3]
值得提醒的是,扩展运算符(…)也可以将某些数据结构转为数组 (上面有提到).
// arguments对象
function foo() {
const args = [...arguments];
}
Array.from还可以接受第二个参数,作用类似于数组的map方法,用来对每个元素进行处理,将处理后的值放入返回的数组.
<script>function fun() {console.log(Array.from(arguments, x => x * x)); // [1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36]// 等同于console.log(Array.from(arguments).map(x => x * x)); // [1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36]}fun(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)</script>
5 Array.of ( )
[ Array.of ]方法用于将一组值,转换为数组.
Array.of(3, 11, 8) // [3,11,8]
Array.of(3) // [3]
Array.of(3).length // 1
这个方法的主要目的,是弥补数组构造函数Array()的不足. 因为参数个数的不同,会导致Array()的行为有差异.
<script>console.log(Array()); // []console.log(Array(3)); // [, , ,]console.log(Array(3, 11, 8)); // [3, 11, 8]
</script>
上面代码中,Array方法没有参数、一个参数、三个参数时,返回结果都不一样. 只有当参数个数不少于 2 个时,Array()才会返回由参数组成的新数组. 参数个数只有一个时,实际上是指定数组的长度.
6 数组的实例方法
1 数组实例的 copyWithin()
数组实例的 [ copyWithin() ] 方法,在当前数组内部,将指定位置的成员复制到其他位置(会覆盖原有成员),然后返回当前数组. 也就是说,使用这个方法,会修改当前数组.
Array.prototype.copyWithin(target, start = 0, end = this.length)
它接受三个参数.
target(必需): 从该位置开始替换数据. 如果为负值,表示倒数.
start(可选): 从该位置开始读取数据,默认为 0.如果为负值,表示从末尾开始计算.
end(可选): 到该位置前停止读取数据,默认等于数组长度. 如果为负值,表示从末尾开始计算.
<script>let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]let arrNew = arr.copyWithin(0, 3);console.log(arrNew); // [4, 5, 3, 4, 5]// 上面代码表示将从 3 号位直到数组结束的成员(4 和 5),复制到从 0 号位开始的位置,结果覆盖了原来的 1 和 2.
</script>
// 将3号位复制到0号位
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5].copyWithin(0, 3, 4) //从三号位开始读取,到四号位结束,得到[4],将其替换到0号位
// [4, 2, 3, 4, 5]// -2相当于3号位,-1相当于4号位
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5].copyWithin(0, -2, -1) //从倒数2号位开始读取,到倒数一号位结束,得到[4],将其替换到0号位
// [4, 2, 3, 4, 5]
2 数组实例的 find() 和 findIndex()
数组实例的 [ find ] 方法,用于找出第一个符合条件的数组成员. 它的参数是一个回调函数,所有数组成员依次执行该回调函数,直到找出第一个返回值为true的成员,然后返回该成员. 如果没有符合条件的成员,则返回 undefined .
<script>let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]let arrNew = arr.find(item => item % 2 === 0);console.log(arrNew); // 2
</script>
数组实例的 [ findIndex] 方法的用法与 [ find ] 方法非常类似,返回第一个符合条件的数组成员的位置,如果所有成员都不符合条件,则返回-1.
<script>let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]let arrNew = arr.findIndex(item => item % 2 === 0);console.log(arrNew); // 1
</script>
3 数组实例的 entries(),keys() 和 values()
ES6 提供三个新的方法——[ entries() ],[ keys() ] 和 [ values() ]——用于遍历数组. 它们都返回一个遍历器对象.可以用for…of循环进行遍历,唯一的区别是[ keys() ]是对键名的遍历、[ values() ]是对键值的遍历,[ entries() ]是对键值对的遍历.
<script>let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]for (let [k, v] of arr.entries()) {console.log(k, v)}// 0 1// 1 2// ...for (let key of arr.keys()) {console.log(key);}for (let value of arr.values()) {console.log(value)}
</script>如果不使用for…of循环,可以手动调用遍历器对象的next方法,进行遍历.
let letter = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
let entries = letter.entries();
console.log(entries.next().value); // [0, 'a']
console.log(entries.next().value); // [1, 'b']
console.log(entries.next().value); // [2, 'c']
4 数组实例的 includes()
[ Array.prototype.includes ] 方法返回一个布尔值,表示某个数组是否包含给定的值,与字符串的 [ includes ] 方法类似. ES2016 引入了该方法.
<script>let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]let res = arr.includes(10);console.log(res); // false</script>
该方法的第二个参数表示搜索的起始位置,默认为0. 如果第二个参数为负数,则表示倒数的位置,如果这时它大于数组长度(比如第二个参数为-4,但数组长度为3),则会重置为从0开始.
<script>let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]let res = arr.includes(1, 2);console.log(res); // false
</script>
5 数组实例的 flat(),flatMap()
数组的成员有时还是数组,Array.prototype.flat()用于将嵌套的数组“拉平”,变成一维的数组. 该方法返回一个新数组,对原数据没有影响.
[ flat() ] 默认只会“拉平”一层,如果想要“拉平”多层的嵌套数组,可以将 [ flat() ] 方法的参数写成一个整数,表示想要拉平的层数,默认为1.
<script>let arr_in_in = [111, 122, 133]let arr_inside = [11, 12, 13, arr_in_in]let arr_outside = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, arr_inside]let flat = arr_outside.flat();console.log(flat); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, Array(3)]
</script>
[ flat() ] 的参数为2,表示要“拉平”两层的嵌套数组.
<script>let arr_in_in = [111, 122, 133]let arr_inside = [11, 12, 13, arr_in_in]let arr_outside = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, arr_inside]let flat = arr_outside.flat(2); // 表示拉两层console.log(flat); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, Array(3)]
</script>
如果不管有多少层嵌套,都要转成一维数组,可以用Infinity关键字作为参数.
<script>let arr_in_in = [111, 122, 133]let arr_inside = [11, 12, 13, arr_in_in]let arr_outside = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, arr_inside]let flat = arr_outside.flat(Infinity); // 全部拉平console.log(flat); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, Array(3)]
</script>
如果原数组有空位, [ flat() ] 方法会跳过空位. --> 这个可以用作去除数组中空位,特殊场景好用
[1, 2, , 4, 5].flat()
// [1, 2, 4, 5]
[ flatMap() ] 方法对原数组的每个成员执行一个函数(相当于执行Array.prototype.map()),然后对返回值组成的数组执行 [ flat() ] 方法. 该方法返回一个新数组,不改变原数组.
<script>let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]let arrNew = arr.flatMap(item => item * item);console.log(arrNew); // [1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100]
</script>
<script>let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]let arrNew = arr.flatMap(item => [item, item * item]);console.log(arrNew); // [1, 1, 2, 4, 3, 9, 4, 16, 5, 25, 6, 36, 7, 49, 8, 64, 9, 81, 10, 100]
</script>
<script>let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]let arrNew = arr.flatMap(item => [[item, item * item]]);console.log(arrNew); //
</script>

6 数组实例的 filter()
filter() 方法创建一个新数组, 其包含通过所提供函数实现的测试的所有元素. 不会改变原有数组
筛选对象数组中符合条件的
<script>const arr = [{look: '帅', name: '@hongjilin'},{look: '很帅', name: '努力学习的汪'}]let arrNew = arr.filter(item => item.name === '努力学习的汪');console.log(arrNew) // {"look":"很帅","name":"努力学习的汪"}
</script>
筛选对象数组中不符合条件的
<script>const arr = [{look: '帅', name: '@hongjilin'},{look: '很帅', name: '努力学习的汪'}]let arrNew = arr.filter(item => item.name !== '努力学习的汪');console.log(arrNew) // {"look":"帅","name":"@hongjilin"}
</script>
去除数组中的空字符串、undefined、null
<script>const undefinedArr = ['这是undefined数组', '2', undefined, '努力学习的汪', undefined]const nullArr = ['这是null数组', '2', null, '努力学习的汪', null]const stringArr = ['这是空字符串数组', '2', '', '努力学习的汪', ''] //空字符串里面不能包含空格let newArr = [] //定义一个新数组来测试承接//过滤 undefinednewArr = undefinedArr.filter(item => item)console.log(newArr) //log: ["这是undefined数组", "2", "努力学习的汪"]//过滤 nullnewArr = nullArr.filter(item => item)console.log(newArr) //log: ["这是null数组", "2", "努力学习的汪"]//过滤空字符串newArr = stringArr.filter(item => item)console.log(newArr) //log: ["这是空字符串数组", "2", "努力学习的汪"]
</script>
数组去重
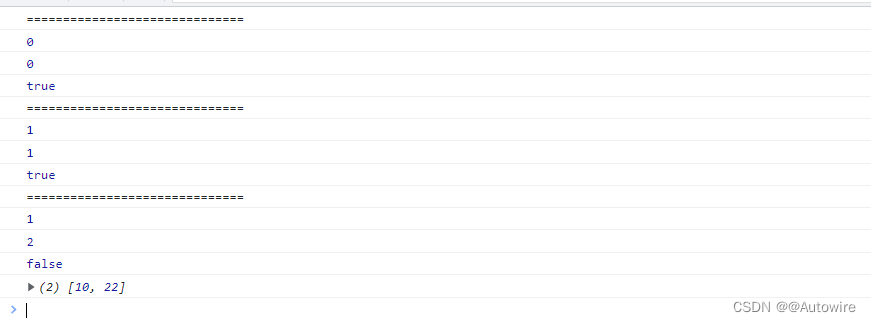
<script>const arr = [10, 22, 22];let arr2 = arr.filter((item, index, self) => {console.log('==============================')console.log(self.indexOf(item))console.log(index)let res = self.indexOf(item) === indexconsole.log(res);return res})console.log(arr2); //[10, 22]
</script>
7 数组实例的 map()
定义: 对数组中的每个元素进行处理,得到新的数组;
特点: 不改变原有数据的结构和数据
<script>const array = [1, 3, 6, 9];const newArray = array.map(item => item + 1); console.log(newArray); //log: [2, 4, 7, 10]console.log(array); //log: [1, 3, 6, 9]
</script>
8 数组实例的 some() 、every()
some() : 方法测试数组中是不是至少有1个元素通过了被提供的函数测试. 它返回的是一个Boolean类型的值.
every(): 方法测试一个数组内的所有元素是否都能通过某个指定函数的测试. 它返回一个布尔值.
<script>const array = [1, 3, 6, 9];let res = array.some(item => item === 3);console.log(res); // truelet res_ = array.every(item => item < 9);console.log(res_); // false
</script>
9 Array.prototype.sort() 的排序稳定性
排序稳定性(stable sorting)是排序算法的重要属性,指的是排序关键字相同的项目,排序前后的顺序不变.
<script>const array = [100, 1, 3, 6, 9];let arrNew = array.sort((a, b) => a - b);console.log(arrNew);
</script>
7 Map
1 接受数组作为参数
Map 也可以接受一个数组作为参数. 该数组的成员是一个个表示键值对的数组.
<script>const map = new Map([['name', '努力学习的汪'],['title', 'Author']]);console.log(map); // {'name' => '努力学习的汪', 'title' => 'Author'}console.log(map.get('name')); // 努力学习的汪console.log(map.get('title')); // Authorconsole.log(map.keys()); // MapIterator{'name', 'title'}console.log(map.values()); // MapIterator{'努力学习的汪', 'Author'}
</script>
2 对同一个键多次赋值,后面的值将覆盖前面的值
<script>const map = new Map();map.set(1, 'zhaoshuai-la').set(1, 'zhaoshuai-lc');console.log(map) // {1 => 'zhaoshuai-lc'}
</script>
3 只有对同一个对象的引用,Map 结构才将其视为同一个键
4 实例的属性和操作方法
<script>let map = new Map();map.set('name', 'zhaoshuai-lc')map.set('age', 26)console.log(map); // {'name' => 'zhaoshuai-lc', 'age' => 26}console.log(map.size); // 2console.log(map.get('name')); // zhaoshuai-lcconsole.log(map.has('name')); // trueconsole.log(map.delete('name')); // trueconsole.log(map); // {'age' => 26}map.clear();console.log(map);
</script>
5 遍历方法
Map 结构原生提供三个遍历器生成函数和一个遍历方法.
Map.prototype.keys(): 返回键名的遍历器.
Map.prototype.values(): 返回键值的遍历器.
Map.prototype.entries(): 返回所有成员的遍历器.
Map.prototype.forEach(): 遍历 Map 的所有成员.
<script>let map = new Map();map.set('name', 'zhaoshuai-lc')map.set('age', 26)let entries = map.entries();console.log(entries); // {'name' => 'zhaoshuai-lc', 'age' => 26}for (let item of entries) {console.log(item); // ['name', 'zhaoshuai-lc']}map.forEach(item => console.log(item)) // zhaoshuai-lc 26
</script>
Map 的遍历顺序就是插入顺序
6 Map 结构转为数组结构
Map 结构转为数组结构,比较快速的方法是使用扩展运算符(…).
<script>let map = new Map([['name', 'zhaoshuai-lc'], ['age', 100]]);console.log(map); // {'name' => 'zhaoshuai-lc', 'age' => 100}console.log(...map.keys()); // name ageconsole.log(...map.values()) // zhaoshuai-lc 100let mapArr_key = [...map][0]let mapArr_value = [...map][1]console.log(mapArr_key); // ['name', 'zhaoshuai-lc']console.log(mapArr_value); // ['age', 100]
</script>
7 Map 的 forEach() 方法
Map 还有一个forEach方法,与数组的forEach方法类似,也可以实现遍历.
<script>let map = new Map([['name', 'zhaoshuai-lc'], ['age', 100]]);map.forEach((item, index, self) => {console.log('item = ' + item + ', index = ', index + ', self = ', self)})
</script>

8 与其他数据结构的互相转换
1 Map 转为数组
前面已经提过,Map 转为数组最方便的方法,就是使用扩展运算符(…).
let map = new Map([['name', 'zhaoshuai-lc'], ['age', 100]]);
console.log(map)
console.log([...map])
/*** Map(2) { 'name' => 'zhaoshuai-lc', 'age' => 100 }[ [ 'name', 'zhaoshuai-lc' ], [ 'age', 100 ] ]*/
2 数组 转为 Map
将数组传入 Map 构造函数,就可以转为 Map.
let map = new Map([['name', 'zhaoshuai-lc'], ['age', 100]]);
console.log(map){ 'name' => 'zhaoshuai-lc', 'age' => 100 }3 Map 转为对象
function mapToObj(strMap) {let obj = {}; //创建一个空对象for (let [k, v] of strMap) {obj[k] = v} //循环遍历并给空对象赋值return obj; //最后将加工好的对象返回出去
}//字符串的键转对象
const map = new Map([['userName', 'zhaoshuai-lc'], ['age', 26]])
console.log(mapToObj(map)); // { userName: 'zhaoshuai-lc', age: 26 }
4 对象转为 Map
对象转为 Map 可以通过Object.entries().
let person = {'userName': 'zhaoshuai','userAge': 26,'sex': 'male'
}let map = new Map(Object.entries(person));
console.log(map); // { 'userName' => 'zhaoshuai', 'userAge' => 26, 'sex' => 'male' }
5 Map 转为 JSON
Map 的键名都是字符串
Map 转为 JSON 要区分两种情况. 一种情况是,Map 的键名都是字符串,这时可以选择转为对象 JSON.
const mapToObj = (map) => {let obj = {};for (let [k, v] of map) {obj[k] = v;}return obj;
}
let map = new Map().set('userName', 'zhaoshuai-lc').set('age', 26);
const objToJson = obj => JSON.stringify(obj);
let obj = mapToObj(map);
let json = objToJson(obj);
console.log(json); // {"userName":"zhaoshuai-lc","age":26}
另一种情况是,Map 的键名有非字符串,这时可以选择转为数组 JSON.
const arrayToJson = array => JSON.stringify(array)
const mapToArray = map => [...map]
let map = new Map().set(true, 1).set({name: '对象'}, ['这是数组']);
let array = mapToArray(map);
let json = arrayToJson(array);
console.log(json);
/*** [[true,1],[{"name":"对象"},["这是数组"]]]*/
6 JSON 转为 Map
let json = '{"userName":"zhaoshuai-lc","age":26}';
let obj = JSON.parse(json);
console.log(obj);
7 map()方法
map(): 映射,即原数组映射成一个新的数组
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
let arrNew = arr.map(item => item * item);
console.log(arrNew);
