网站开发的选题依据保定seo外包服务商
随着城市化发展,很多乡村设施也在逐渐完善,智能监控也成了乡村发展必不可少的一环,智能视频监控应该在乡村建设里如何发挥作用呢?
1、有效提升安全意识
通过在乡村重要区域、公共场所、道路等设置智能视频监控设备,可以有效监控和防范潜在的安全威胁,如盗窃、破坏等。这一举措将提高居民的安全意识和安全感,为乡村的稳定和安宁做出贡献。

2、预防和解决问题
旭帆科技AI智能视频监控技术可以提供实时的图像和视频,帮助乡村管理人员及时发现和解决问题,如交通事故、火灾等紧急情况,还支持实时调阅与查看,利于事后取证。
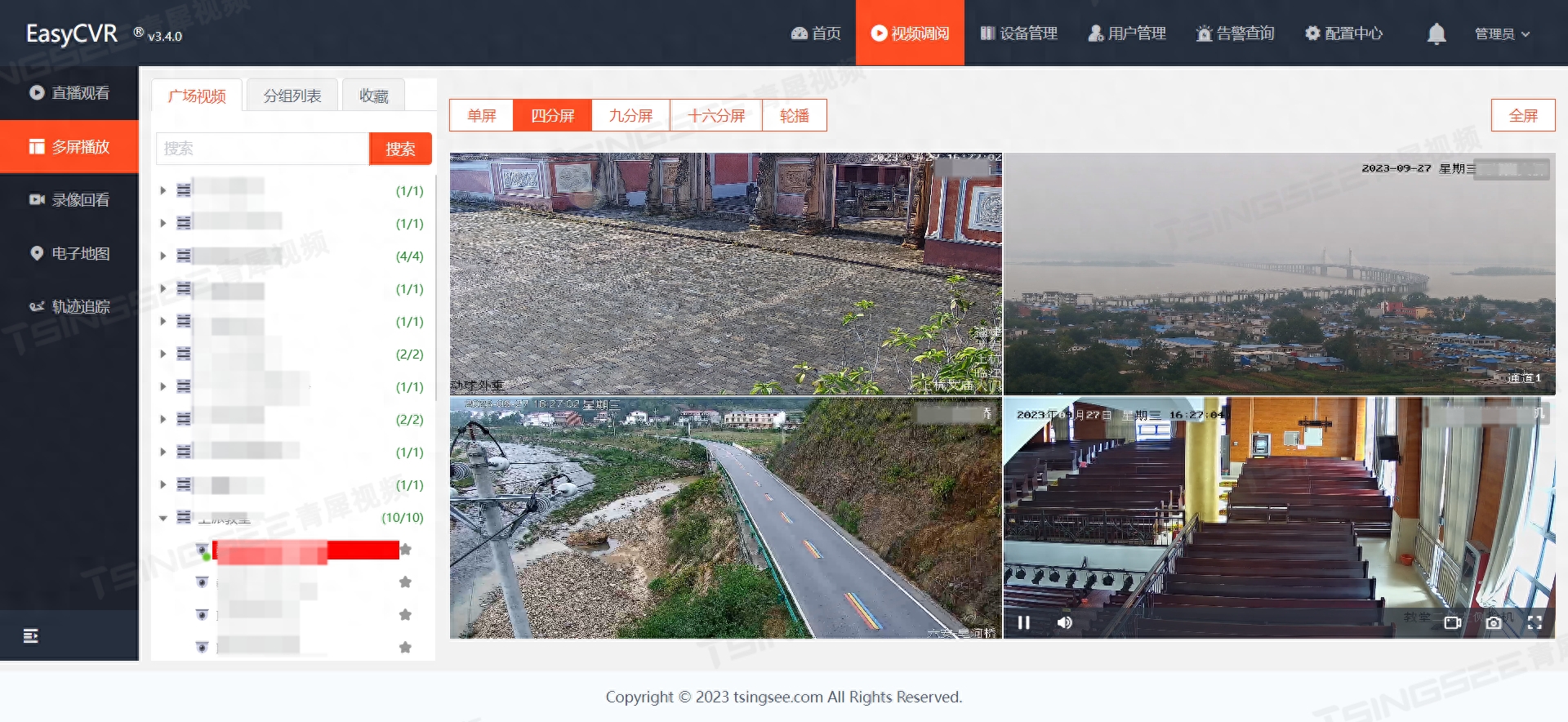
利用安防监控系统EasyCVR视频汇聚平台的视频能力,可以对村庄重点区域、道路等进行全天候24小时可视化监管,平台可以提供实时视频监控、视频录像、检索与回放、云存储、视频集中存储、磁盘阵列存储、云台控制等功能。此外,视频监控系统EasyCVR还能支持通过平台级联功能将视频数据共享给上级乡镇监控中心。
3、促进社会治安
乡村社会治安是乡村发展的关键因素之一。智能视频监控可以提供重要的证据和线索,帮助警方追踪和解决犯罪行为,维护社会治安,确保居民的安全。例如安防监控系统EasyCVR可提供历史录像回放功能,当发生异常事件时,通过历史录像回放还原现场经过,起到有效的事件追溯作用。
4、旅游和文化保护
乡村经常有许多美丽的风景和历史文化遗产,这对于乡村旅游和文化保护至关重要。前端视频监控设备可接入TSINGSEE青犀视频监控系统EasyCVR平台或者EasyDSS视频直播点播系统,对乡村美好风景进行直播、点播等,在对外宣传方面有着极大帮助。
5、促进信息共享
智能视频监控系统可以与其他数字化基础设施相结合,如互联网、移动应用等,实现信息共享和互联互通。这有助于提高乡村的管理效率和服务质量,同时也方便居民获取信息和享受便利的服务。
智能视频监控作为一种技术手段,结合乡村的实际需求和发展目标,可以为乡村的安全、发展和治理提供有效支持,促进乡村实现美好的未来。
